SkyBase
Contents
Overview
SkyBase is a database that stores the homology models built by SkyLine analysis for
- structures in the RCSB Protein Data Bank (PDB) with a 60% redundancy cutoff (PDB60)
- structures in the Northeast Structural Genomics Consortium database
As of 7/19/2012, the databases have:
- PDB60: 12,264 structures, 7,804,258 models.
- NESG: 946 structures, 1,943,390 models.
Users can search the database with their sequence of interest to find homology models which meet user-defined alignment coverage and sequence identity constraints.
SkyBase Web Version
SkyBase can be used either within geWorkbench, or directly in a web browser. For more information about the web version, please see the following two links.
SkyBase Web Tutorial
http://skybase.c2b2.columbia.edu/nesg3/help/help.html
SkyBase Web Search Page
http://skybase.c2b2.columbia.edu/nesg3/nesg.php
SkyBase in geWorkbench
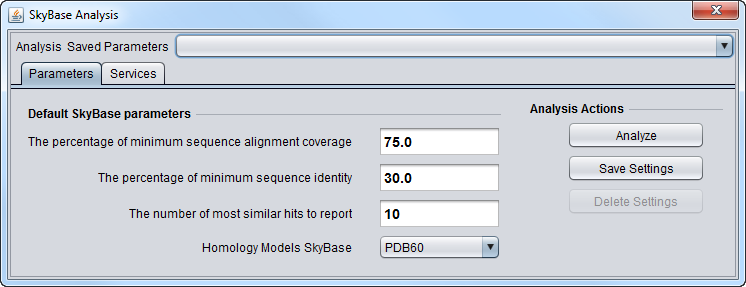
Parameters
BLAST is run using the query sequence to identify "hits" to existing models in the SkyBase database.
% Minimum Alignment Coverage
- Percentage of the hit sequence that the query sequence must align to, including similarity matches.
- If the query sequence is shorter than hit sequence, sequence coverage is calculated for the query sequence.
% Minimum Sequence Identity
Percentage of the hit sequence that the query sequence must have exact letter matches with.
Most Similar Hits to Report
The number of top hits to report, based on a calculated rank. The rank combines the model quality pG, the template coverage, and the model-template sequence identity.
- Models with a quality score < 0.7 are discarded.
- The remaining models are then binned by the quality score, pG, such that bin A > bin B > bin C:
- 0.9 <= pG < 1.0, bin A
- 0.8 <= pG < 0.9, bin B
- 0.7 <= pG < 0.8, bin C
- Within each bin, ranks are further decided by sorting their template coverage; higher coverage gets higher rank
- Within each bin, for any models with the same template coverage, ranks are further decided by sorting the hits on their sequence identity; higher identity gets higher rank.
The BLAST search with the parameters shown below will return the top 10 results that have at least a 75% sequence coverage of hit sequences (if the query sequence is shorter than hit sequence, sequence coverage is calculated for the query sequence) and over 30% sequence identity of the two sequences.
Homology Models SkyBase
For details of the two supported homology model databases, please see http://skybase.c2b2.columbia.edu/nesg3/help/help.html
- PDB60 (default) - models generated based on structures in the PDB with a 60% redundancy cutoff.
- NESG - models generated based on structures in the Northeast Structural Genomics Consortium database (~670 structures).
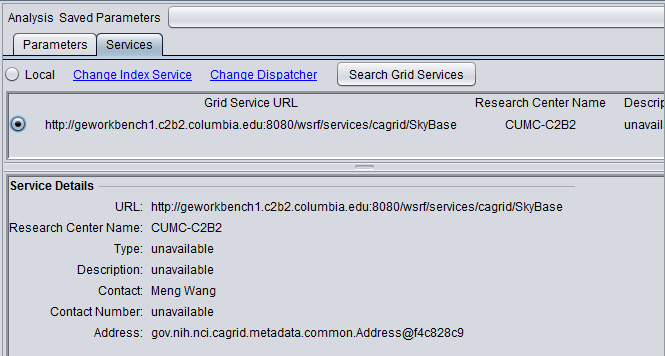
Grid Service
No local service implementation of SkyBase is available in geWorkbench. Instead, an open grid service is used. No username or password is required.
In the Services tab,
- Click on "Search Grid Services". This will retrieve the information for the SkyBase grid service from the index service.
- Select the radio button in front of the SkyBase grid service.
- Return to the "Parameters" tab.
Running a SkyBase query
- Make sure SkyBase is loaded in the Component Configuration Manager.
- Load a protein sequence file for which you wish to find homology models.
- Select the SkyBase analysis component in the Control area of geWorkbench.
- Set the parameters as desired.
- Select the grid service in the "Services" tab (there is no local service).
- Back on the Parameters tab, hit "Analyze".
Viewing SkyBase Results
Note - SkyLine results are maintained on the server, not in geWorkbench. Each time a different structure is selected for viewing, its details will be retrieved from the SkyBase server. While there is currently no data deletion policy, data of interest should be saved to disk or screenshots taken.
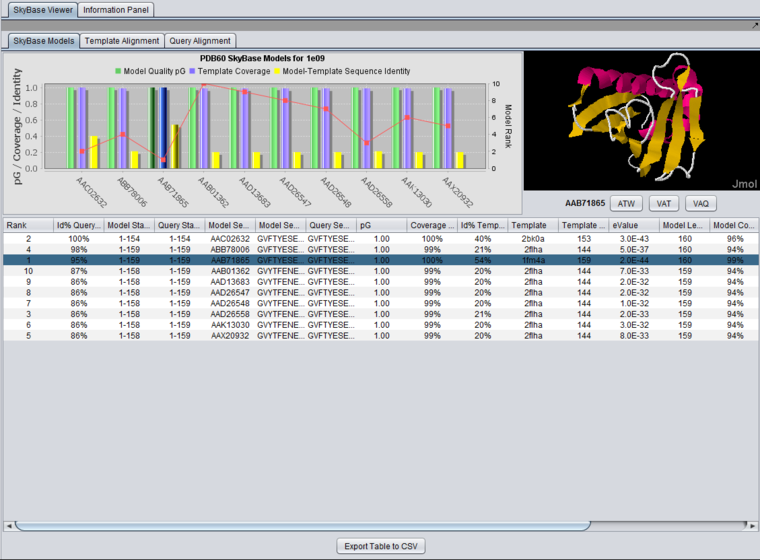
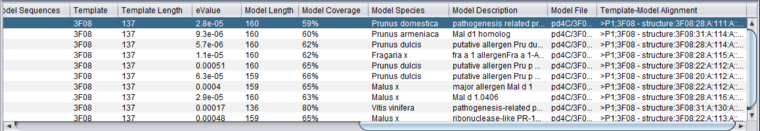
After query with the sequence for PDB structure "1e09", 1e09.fasta:
Table
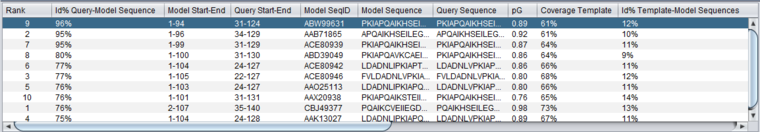
Column Headers
- %Id Query-Model Sequence - Percent identity in the query-model sequence alignment.
- Model Start-End
- Query Start-End
- Model SeqID
- Model Sequence
- Query Sequence
- pG - a log-transformed, length-normalized integration over the residue-by-residue Prosa II profile [Sippl, 1993].
- Coverage Template
- %Id Template-Model Sequences - Percent identity in the template-model sequence alignment.
- Template
- Template Length
- eValue
- Model Length
- Model Coverage
- Model Species
- Model Description
- Model File
- Template-Model Alignment
Note on column sorting
In the initial display, the data is sorted in descending order on the second column, "Id% query-model-sequence". The table can be resorted based on any column by clicking on that column's header. Repeated clicks on the same header will cycle through sorting the table in three ways:
- Original order (column 2, descending).
- Ascending order of clicked-on column.
- Descending order of clicked-on column.
Table Column Details, upper left
Table Column Details, upper right
- Export to CSV - Export of the table to a CSV format file is available from a right-click menu on the table itself, or using the "Export Table to CSV" button at the bottom of the table. The data is exported in the same order in which it is displayed.
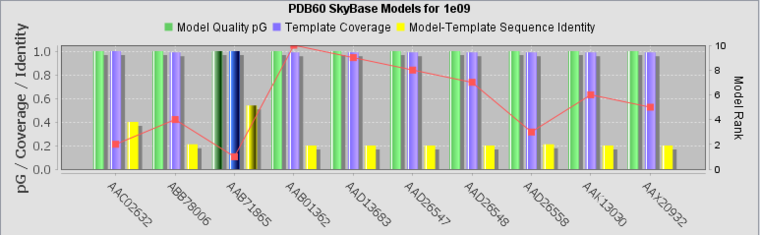
Bar Chart
For each model, the bar chart plots several of the most important features for easy comparison:
- Model Quality, pG - a log-transformed, length-normalized integration over the residue-by-residue Prosa II profile [Sippl, 1993].
- Template Coverage -
- Model-Template Sequence Identity - Degree of identity between the model sequence and the structural template.
- Rank - red line, not labeled.
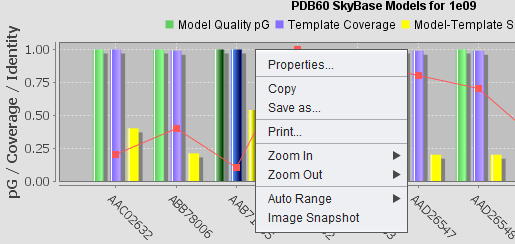
Right-clicking on the chart will produce a pop-up menu with standard controls.
- Properties - adjust the appearance of the chart.
- Copy - copy an image of the chart to the clipboard for pasting into another application such as Word.
- Save as - Save an image of the chart in PNG format.
- Print - print the chart.
- Zoom in, zoom out - range axis only. Can also zoom in and out using mouse left-click right and left drag motion.
- Auto range - readjust chart to fit all data.
- Image Snapshot - save an image of the chart to the Workspace.
Alignments
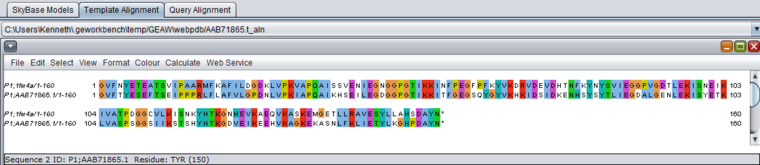
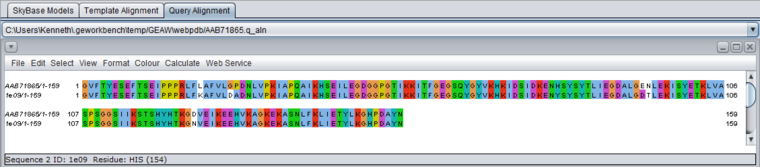
Jalview - Alignments between the model and the original template sequence, and between the model and the query sequence, can be viewed using the built-in Jalview multiple alignment viewer. http://www.jalview.org/. The residues are color-coded in the alignments.
This viewer offers a number of options for customizing the alignment view.
Model-template alignment (VAT)
Model-query alignment (VAQ)
Controls
- ATW - Add Structure to Workspace- The "ATW" button will add the currently displayed protein structure file (PDB file) as a new node in the Workspace.
- VAT - View alignment between model and template - display the model-template sequence alignment in Jalview.
- VAQ - View alignment between model and query - display the model-query sequence alignment in Jalview.
- Export Table to CSV - Export the entire table as a CSV format file. The data is written to file in the same order in which it is displayed on screen (e.g. after sorting).
Exceptions
- If a number, such as pG is not valid or missing, a zero will be substituted.
- Missing PDB files and missing sequence alignments are properly handled.
References
Lee H, Li Z, Silkov A, Fischer M, Petrey D, Honig B, Murray D. (2010) High-throughput computational structure-based characterization of protein families: START domains and implications for structural genomics. J Struct Funct Genomics. 11(1):51-9. Link to paper
Mirkovic N., Li Z., Parnassa A., Murray D. (2007) Strategies for High-Throughput Comparative Modeling: Applications to Leverage Analysis in Structural Genomics and Protein Family Organization. Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics 66:766-777. link.
Sippl MJ (1993) Recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Proteins. 17(4):355–62. link