Difference between revisions of "Fold Change"
(→Calculation Method) |
(→Difference of average log2 values) |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
====Difference of average log2 values==== | ====Difference of average log2 values==== | ||
* Calculated with log2 values. Linear data will be transformed to log2. | * Calculated with log2 values. Linear data will be transformed to log2. | ||
| + | * Because of the log2 transformation of linear data, no linear value should be less than or equal to zero. If such a value is encountered, a warning will be issued and the analysis terminated. | ||
* For each marker, calculate Avg(log2(Case arrays)) - Avg(log2(Control arrays)). | * For each marker, calculate Avg(log2(Case arrays)) - Avg(log2(Control arrays)). | ||
* Here, if the Case arrays have lower expression than the Control, the negative sign results directly. | * Here, if the Case arrays have lower expression than the Control, the negative sign results directly. | ||
Revision as of 16:39, 1 June 2011
Contents
Overview
(The Fold Change component was inadvertently omitted from geWorkbench release 2.2.0. It is available in the development version).
Fold change is used to compare the expression of genes between two sets of arrays, e.g. case and control sets.
This component allows a threshold for fold-change to be set. Markers that exceed the threshold are placed into new sets in the Markers component - one for those with positive fold-change, the other for negative (where the inverse is above threshold).
Two methods are provided to calculate fold change. The component also allows either calculation to be carried out starting with either linear or log2-transformed data.
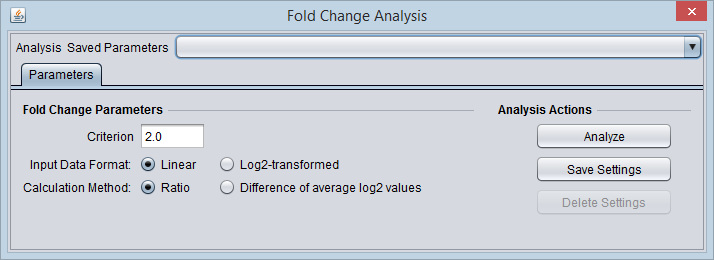
Options
Input Data Format
To correctly calculate the chosen fold-change value, the component must know if the data is linear or log2 transformed. This must be specified by the user.
- Linear
- Log2-transformed
Calculation Method
Ratio
- The ratio of case to control is calculated with linear values. Log2 data will first be transformed to linear.
- For each marker, calculate Avg(Case arrays) / Avg(Control arrays).
- Ratios less than 1 are inverted and given a negative sign, e.g. 0.25 is reported as -4.
Difference of average log2 values
- Calculated with log2 values. Linear data will be transformed to log2.
- Because of the log2 transformation of linear data, no linear value should be less than or equal to zero. If such a value is encountered, a warning will be issued and the analysis terminated.
- For each marker, calculate Avg(log2(Case arrays)) - Avg(log2(Control arrays)).
- Here, if the Case arrays have lower expression than the Control, the negative sign results directly.