Difference between revisions of "MarkUs"
(→Running MarkUs) |
(→Running MarkUs) |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
2. Load a PDB file for the protein whose structure you would like to analyze. | 2. Load a PDB file for the protein whose structure you would like to analyze. | ||
| − | 3. Set the desired parameters. | + | 3. Set the desired parameters. Note that some analyses have check-boxes next to them which are grayed-out. These analyses are always run as part of a MarkUs job and cannot be left out. |
| − | |||
| − | Note that some analyses have check-boxes next to them which are grayed-out. These analyses are always run as part of a MarkUs job and cannot be left out. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
4. Inspect and adjust if desired the parameters to DelPhi. DelPhi calculates the electrostatic field around the molecule. | 4. Inspect and adjust if desired the parameters to DelPhi. DelPhi calculates the electrostatic field around the molecule. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
5. MarkUs is available in geWorkbench as a local or grid service. One advantage of the grid service is that job submission is fully asynchronous. | 5. MarkUs is available in geWorkbench as a local or grid service. One advantage of the grid service is that job submission is fully asynchronous. | ||
| Line 75: | Line 67: | ||
7. Push the "Analyze" button. | 7. Push the "Analyze" button. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
8. The result of the analysis is returned to a web-browser window displayed within geWorkbench. | 8. The result of the analysis is returned to a web-browser window displayed within geWorkbench. | ||
Revision as of 14:50, 15 June 2011
Contents
Overview
MarkUs is a web server to assist the assessment of the biochemical function for a given protein structure. MarkUs identifies related protein structures and sequences, detects protein cavities, and calculates the surface electrostatic potentials and amino acid conservation profile. The results can be browsed by an interactive web interface that allows one to integrate Gene Ontology terms, UniProt features, and the Enzyme Classification. The MarkUs website is at http://luna.bioc.columbia.edu/honiglab/mark-us/cgi-bin/submit.pl.
MarkUs is available as a local or grid service in geWorkbench. Details about running grid services are available in the Grid Services tutorial.
Parameters
Main
DelPhi
ConSurf
Retrieve Prior Jobs
Running MarkUs
The starting point for a MarkUs analysis is a PDB protein structure file.
1. If the MarkUs component has not been loaded in the Component Configuration Manager (CCM), first do so.
2. Load a PDB file for the protein whose structure you would like to analyze.
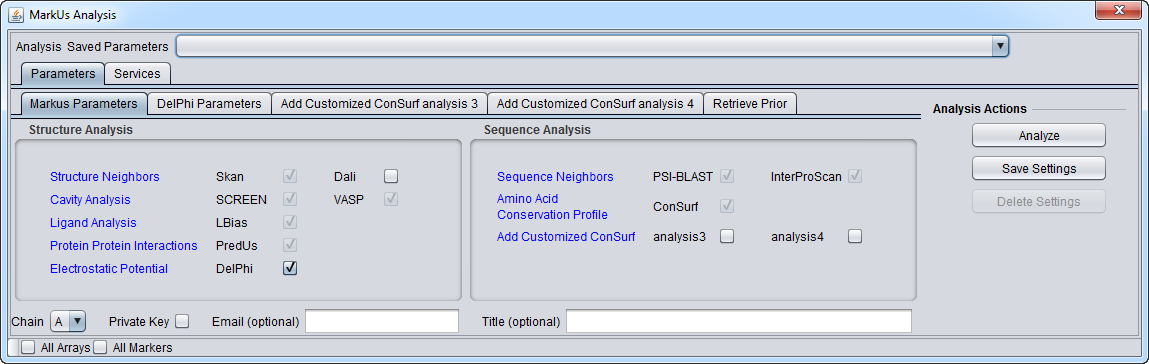
3. Set the desired parameters. Note that some analyses have check-boxes next to them which are grayed-out. These analyses are always run as part of a MarkUs job and cannot be left out.
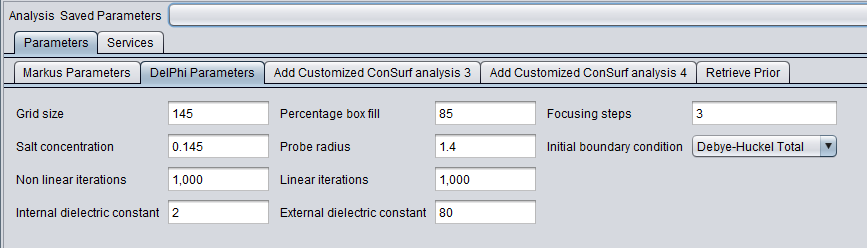
4. Inspect and adjust if desired the parameters to DelPhi. DelPhi calculates the electrostatic field around the molecule.
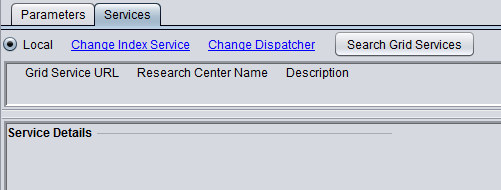
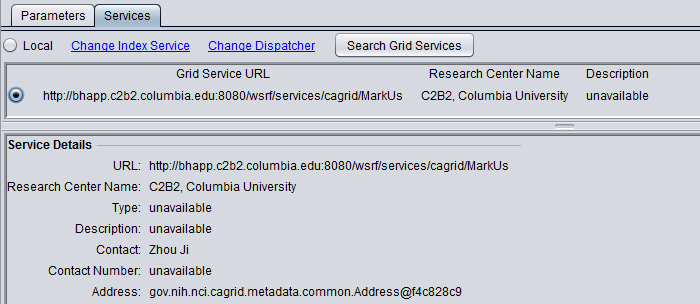
5. MarkUs is available in geWorkbench as a local or grid service. One advantage of the grid service is that job submission is fully asynchronous.
The figure below shows the local service as selected.
To select the grid service for MarkUs,
- Click on the Services tab.
- Push the "Grid Services" button. This will retrieve available MarkUs grid services from an index server.
- Select the radio button for the desired grid service.
6. Return to the Parameters tab.
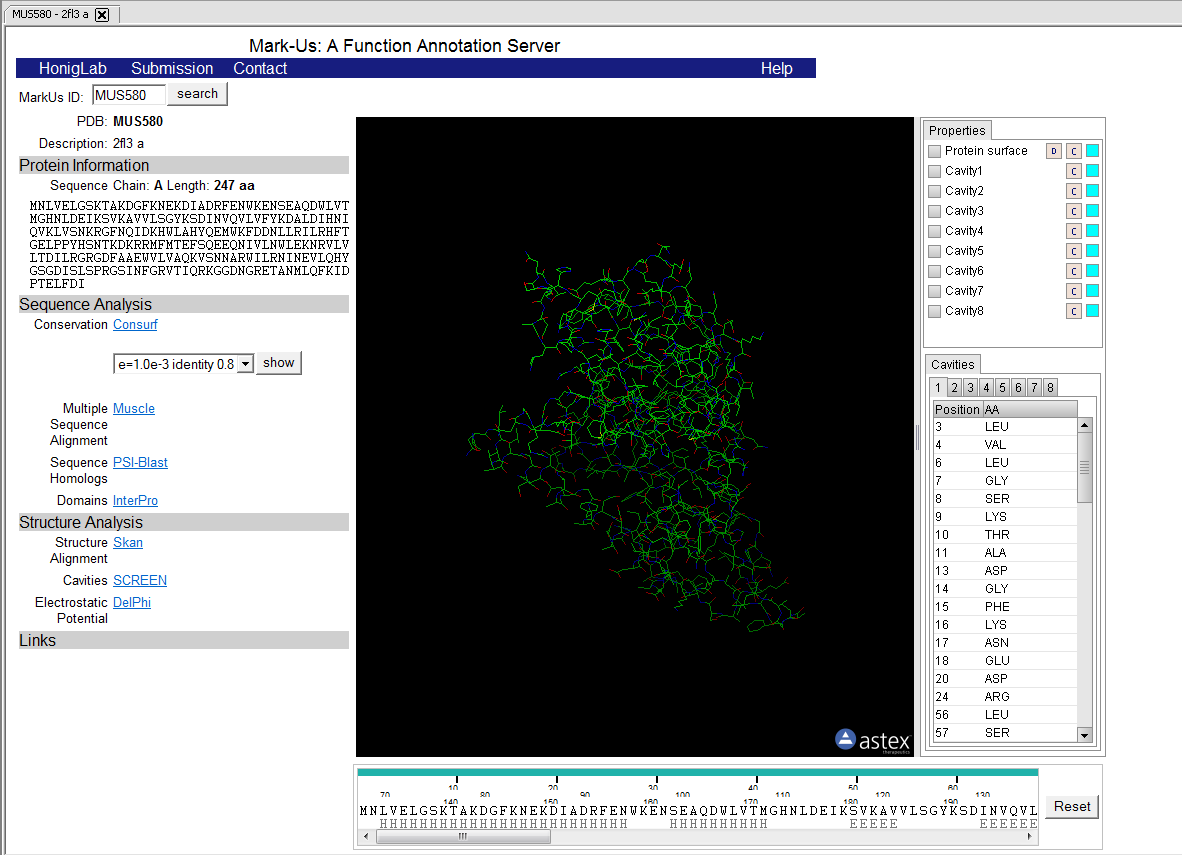
7. Push the "Analyze" button.
8. The result of the analysis is returned to a web-browser window displayed within geWorkbench.
Services (Grid)
See the Grid Services section for further details on setting up a grid job.
MarkUs Server Documentation
Direct Submission of a job to the MarkUs server
http://luna.bioc.columbia.edu/honiglab/mark-us/cgi-bin/submit.pl
This page contains a concise description of the goals of the MarkUs server and a link to the direct web job submission page.
MarkUs Server NESG tutorial
http://luna.bioc.columbia.edu/honiglab/nesg/documentation/tutorial.html
Step by step illustration of submitting a job and interpreting the results.
Detailed Overview of MarkUs Analysis
http://luna.bioc.columbia.edu/honiglab/nesg/documentation/index.html
Describes each aspect of the Markus analysis results and their presentation.