Difference between revisions of "SVM"
(→Running an analysis) |
(→SVM Results Viewer) |
||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
==SVM Results Viewer== | ==SVM Results Viewer== | ||
| + | ===Train tab=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The generated classifier is applied to the original training data set and the results are shown | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''Array Name''' - each array included in the training data set is listed. | ||
| + | * '''Real Class''' - the classification as "Case" or "Control" in the training data set. | ||
| + | * '''Predicted Class''' - The predicted class resulting from applying the generated classifier to each array. | ||
| + | * '''Confidence''' - The confidence associated with the predicted class. | ||
| + | * '''Correct''' - Whether the predicted class agrees with the actual, known classification. A green check mark indicates agreement. | ||
| − | |||
[[Image:SVM_Train_Result.png]] | [[Image:SVM_Train_Result.png]] | ||
Revision as of 15:15, 8 March 2011
Contents
Introduction
The Support Vector Machines (SVM) module implements the support vector machines algorithm. It is a supervised classification method that computes a maximal separating hyperplane between the expression vectors of different classes or phenotypes. Given microarray data with n markers per sample, SVM outputs a hyperplane,W, which can be thought of as a vector with n components each corresponding to the expression of a particular marker. Loosely speaking, assuming that the expression values of each marker have similar ranges, the absolute magnitude of each element in W determines its importance in classifying a sample.
In geWorkbench, the SVM computation compares one or more sets of arrays marked as "Case" against sets marked "Control".
The classifier that is generated can be applied to a test data set. This can be done in two ways. Before generating the classifier, additional arrays sets can be marked as "test". The new classifier will be applied immediately to the "test" data set. Or, after the classifier has been generated, "test" data nodes can be selected using a browser directly in the SVM component.
The result in either case is that the arrays in "test" set will be called as either belonging to the "Case" or "Control" categories, and a confidence value is indicated.
Parameters
The SVM module has no settable parameters for the computation.
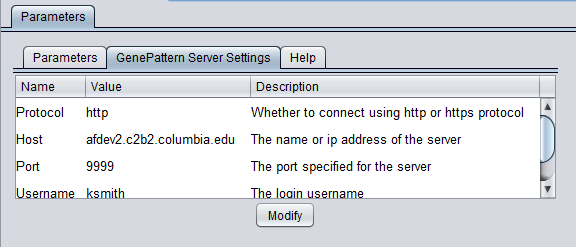
GenePattern Server Settings
To run GenePattern components, a GenePattern account is required.
- Protocol: HTTP or HTTPS, depending on the server being used.
- Host: URL of a GenePattern server.
- Port: Port at which the GenePattern server is located on the Host machine.
- Username: A valid user name on the specified GenePattern server.
- Password: A password, if required by the specified server.
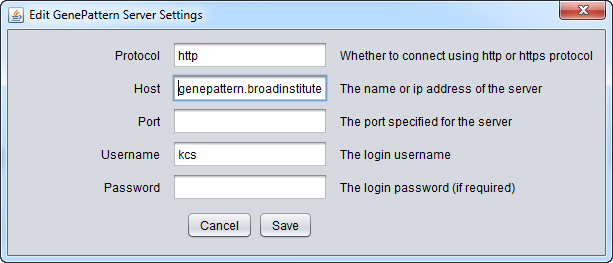
- Modify - change any of the GenePattern connection settings.
Pushing "Modify" brings up an editing box where any of the settings can be changed.
Help
GenePattern components in geWorkbench have their own brief built-in Help section.
Running an analysis
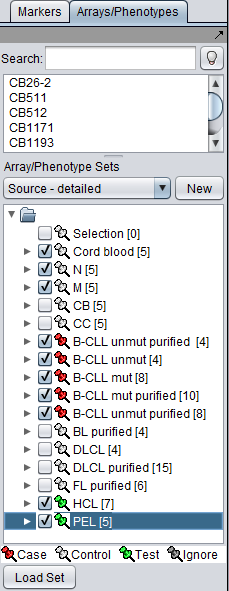
The SVM classifier requires that at least two sets of markers be activated in the Markers component. At least one must be marked as "Case" and at least one must be marked as "Control".
In addition, one or more additional sets can be activated an marked as "Test". After the classifier has been built using the "Case" and "Control" sets, it will be run on the "Test" set if one or more have been specified.
When "Analyze" is pushed, the data is transfered to the GenePattern server, and then the classifier will be run.
Training Classifier running:
Test classifier running:
The resulting classifier is placed into the Project Folders component.
SVM Results Viewer
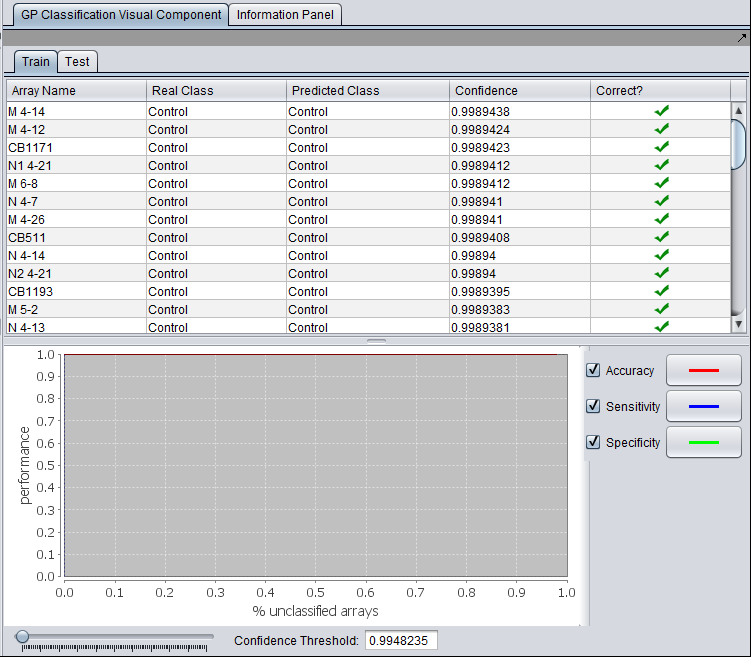
Train tab
The generated classifier is applied to the original training data set and the results are shown
- Array Name - each array included in the training data set is listed.
- Real Class - the classification as "Case" or "Control" in the training data set.
- Predicted Class - The predicted class resulting from applying the generated classifier to each array.
- Confidence - The confidence associated with the predicted class.
- Correct - Whether the predicted class agrees with the actual, known classification. A green check mark indicates agreement.
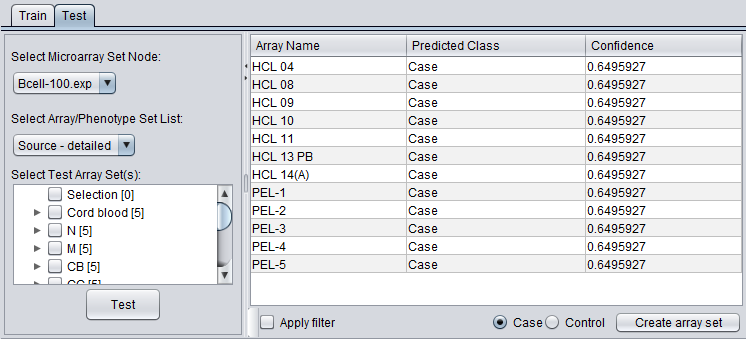
If a test set was used, the results of running the classifier on it are shown in under the "Test" tab.
In addition, a data node browser allows array sets from any microarray data node to be selected. The classifier can then be applied to the selected array set.
References:
- R. Rifkin, S. Mukherjee, P. Tamayo, S. Ramaswamy, C-H Yeang, M. Angelo, M. Reich, T. Poggio, E.S. Lander, T.R. Golub, J.P. Mesirov, An Analytical Method for Multiclass Molecular Cancer Classification, SIAM Review, 45:4, (2003).
- T. Evgeniou, M. Pontil, T. Poggio, Regularization networks and support vector machines, Adv. Comput. Math., 13 (2000), pp. 1-50.
- V. Vapnik, Statistical Learning Theory, Wiley, New York, 1998.