Cellular Networks KnowledgeBase
|
Home | Quick Start | Basics | Menu Bar | Preferences | Component Configuration Manager | Workspace | Information Panel | Local Data Files | File Formats | caArray | Array Sets | Marker Sets | Microarray Dataset Viewers | Filtering | Normalization | Tutorial Data | geWorkbench-web Tutorials |
Analysis Framework | ANOVA | ARACNe | BLAST | Cellular Networks KnowledgeBase | CeRNA/Hermes Query | Classification (KNN, WV) | Color Mosaic | Consensus Clustering | Cytoscape | Cupid | DeMAND | Expression Value Distribution | Fold-Change | Gene Ontology Term Analysis | Gene Ontology Viewer | GenomeSpace | genSpace | Grid Services | GSEA | Hierarchical Clustering | IDEA | Jmol | K-Means Clustering | LINCS Query | Marker Annotations | MarkUs | Master Regulator Analysis | (MRA-FET Method) | (MRA-MARINa Method) | MatrixREDUCE | MINDy | Pattern Discovery | PCA | Promoter Analysis | Pudge | SAM | Sequence Retriever | SkyBase | SkyLine | SOM | SVM | T-Test | Viper Analysis | Volcano Plot |
Contents
- 1 Overview
- 2 General
- 3 Requirements
- 4 The CNKB graphical interface
- 5 Working with the CNKB graphical interface
- 6 Example - Creating an interaction network and viewing it in Cytoscape
- 7 Enhancements coming in geWorkbench v2.2
- 8 Appendix - Data Sources
- 9 References
Overview
This material describes the graphical interface and functionality of the CNKB component released with geWorkbench 2.1.0. Significant enhancements have been made with each recent release.
General
The Cellular Network Knowledge Base (CNKB) is a repository of molecular interactions, including ones both computationally and experimentally derived. Sources for interactions include both publicly available databases such as BioGRID and HPRD, as well as reverse-engineered cellular regulatory interactomes developed in the lab of Dr. Andrea Califano at Columbia University.
Each pairwise interaction may have an associated likelihood indicator (a value between 0 and 1) or another dataset-specific metric reflecting the strength of the underlying data, whether experimental or computational. Details on the methodology used to construct the CNKB are available in Mani et al. 2008.
Gene interaction information from the CNKB can be used, for example, in order to assess the plausibility of a hypothesis of concerted molecular action represented by a gene set that has been discovered using computational approaches (e.g., by running a clustering analysis on a microarray set to identify tandems of co-expressed genes). If the genes in such a set are reported in the CNKB to have several direct interactions (or several common targets) then this may be evidence that the gene set indeed reflects at some level a real biological process.
The CNKB component allows the user to select a group of markers of interest, specify the interaction types (e.g. Protein-Protein, Protein-DNA etc.), and choose a particular interaction data source. After a query of the Knowledge Base, results are displayed both in the CNKB component and as interaction graphs in the Cytoscape component.
Requirements
Both queries against the CNKB database, and display of gene annotation information require that an annotation file be associated with the microarray dataset at the time that it is loaded. See Local Data Files and File Formats for further information.
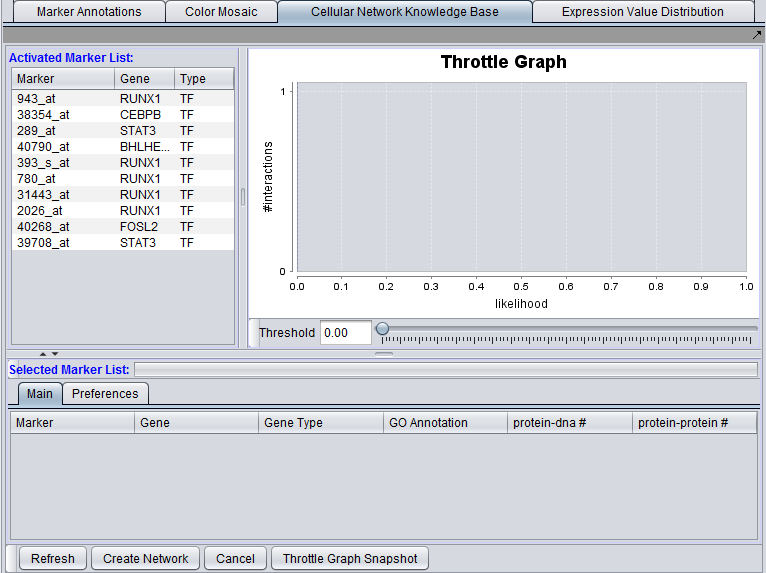
The CNKB graphical interface
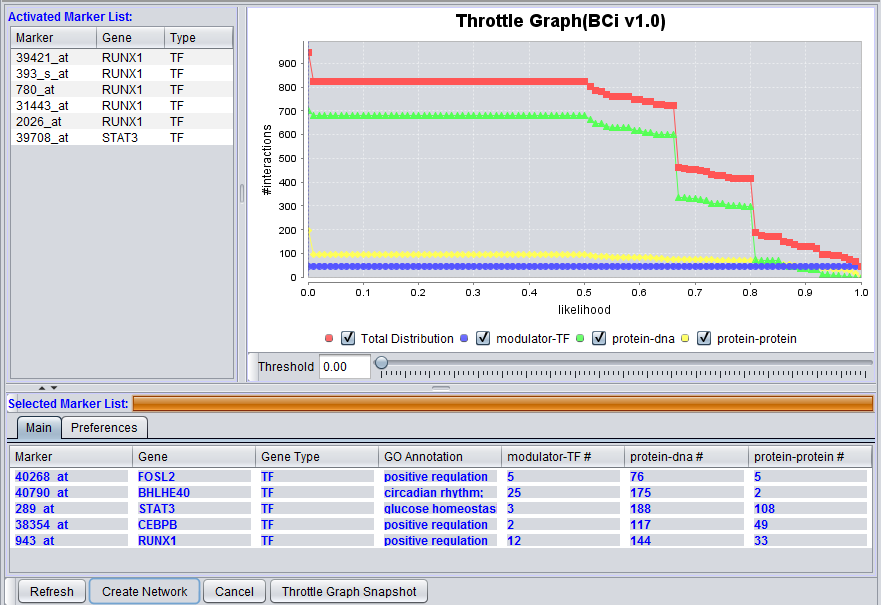
The graphical user interface (GUI) of the CNKB component has three areas of distinct functionality: The "Activated Marker List", the "Selected Marker List", and the "Throttle Graph". The data source, version, and interaction types are specified on a separate "Preferences" tab.
The "Activated Marker List" displays markers activated in the Markers component. From this list, the user can select markers to use in querying the CNKB database. This can be done either by double-clicking on desired markers, or through use of a right-click menu (see below); those selected will be added to the "Selected Marker List" just below.
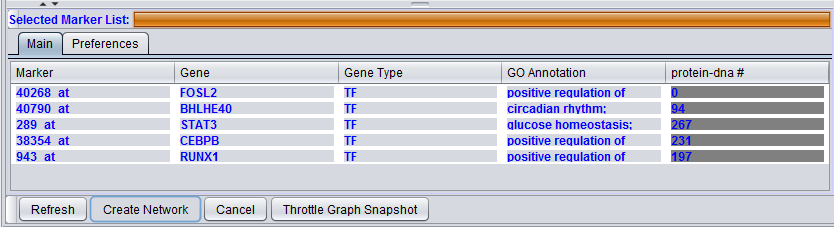
In the "Selected Marker List", the "Main" tab displays which markers will be used in the query, and also displays the query results. Query details are set up in the "Preferences" tab.
Interactions which will be used to build a network graph can be adjusted using the "Throttle Graph". It is used to set a minimum likelihood threshold for inclusion in the network.
A query against the CNKB database is initiated by clicking on the "Refresh" button. All pairwise interactions in the chosen data source of the desired types(s) that involve any marker in the "Selected Marker List" are retrieved.
An interaction network can be constructed by pushing the "Create Network" button. The network will be placed as an adjacency matrix in the Project Folders component and will be automatically displayed in the Cytoscape component.
Working with the CNKB graphical interface
The figures in this section correspond to the example in the final section of this tutorial.
Activated Marker List
The "Activated Marker List" contains the markers that belong to activated marker sets from the Markers component. It contains 3 columns:
Marker
The marker (probeset) name (comes from the microarray set node selected in the Project Folders area).
Gene
The gene name corresponding to the marker, if loaded from an annotation file.
Type
A gene type designation, derived from the gene's GO annotation:
- TF - Transcription Factor,
- K - Kinase,
- P - Phosphatase, and
- (no entry) - type is unknown.
Selecting Markers for Query
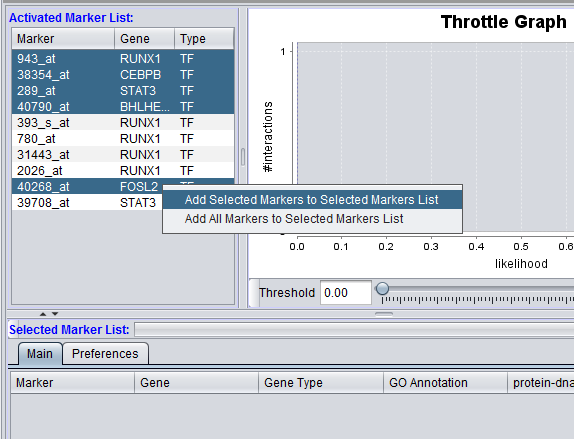
Individual markers in the Activated Marker List can be moved to the Selected Markers List by double-clicking on them.
Right-clicking on the list of markers brings up a menu with two choices:
- Add selected markers to the selected markers list.
- Add all markers to the selected markers list.
For the former case, shown in the figure above, multiple markers can first be highlighted in the usual way by left-clicking on them while holding down the Shift or Control keys. Then, right-click on the list to get the "Add selected markers to the selected markers list" choice.
Selected Marker List
Main
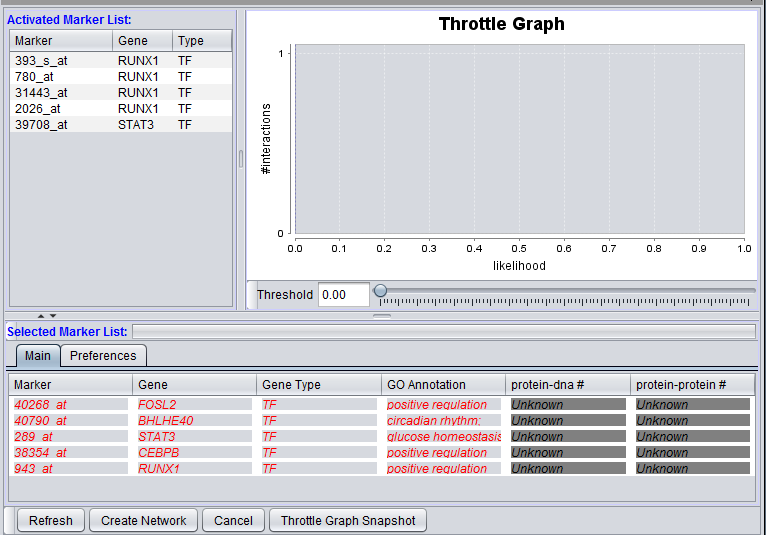
Markers which have been moved from the Activated Markers List to the Selected Markers List can be used to query the CNKB database. Until a query is run, the list items are shown in red italics.
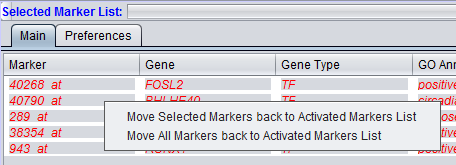
Items that have been added to the Selected Markers list can be removed and sent back to the Activated Markers list by double clicking on their entries or through a right-click menu. The right-click menu (shown below) gives the choice of moving only highlighted, or all markers back to the Activated Markers list.
After a query has been run against the CNKB database, the marker entries are shown in regular font, blue letters.
The Selected Marker List table contains the following columns:
Marker
The marker (probeset) name.
Gene
The gene name corresponding to the marker, if loaded from an annotation file (same as in the "Activated Marker List").
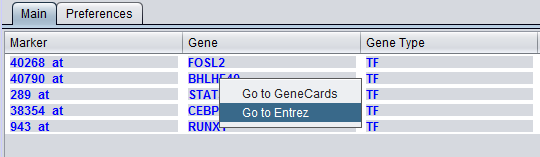
Right-clicking on a gene name will provide link-outs to Gene Cards and Entrez Gene.
Gene Type
A gene type designation, derived from the gene's GO annotation. The list of type codes is the same as that under Type under "Activated Marker List":
- TF - Transcription Factor,
- K - Kinase,
- P - Phosphatase, and
- (no entry) - type is unknown.
GO Annotation
The Gene Ontology (GO) annotation of the gene. Term are annotated to specific markers in the microarray annotation file, and the term descriptions originate in the gene ontology file.
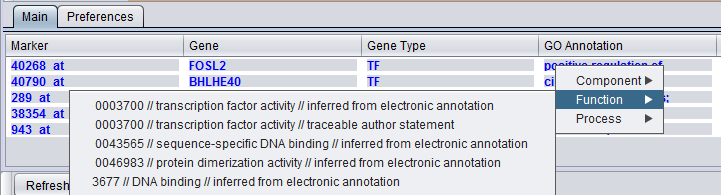
Right clicking on the column brings up the the gene GO classification of the gene across the 3 top-level GO categories: Component, Function and Process.
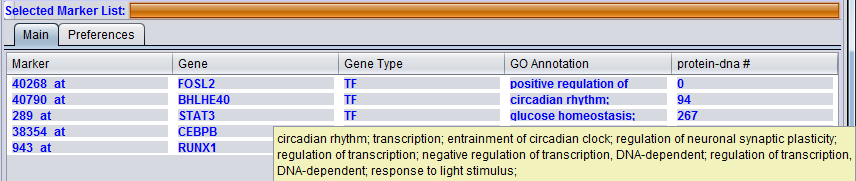
Hovering the mouse cursor over an entry in the GO Description column will display a short summary of the Gene Ontology terms associated with that entry.
More extensive GO annotations can be viewed for desired genes in the Selected Marker list by right-clicking on its entry. A pop-up menu will offer a choice of the three categories of GO annotation: Component, Function and Process. Expanding one of these terms will show the available annotations for that gene.
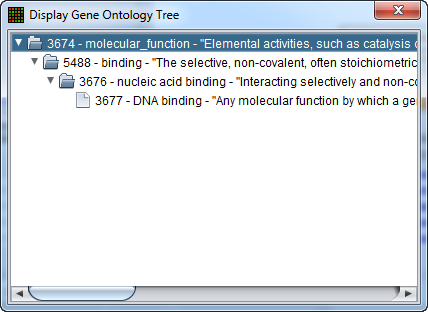
In turn, clicking on one of the terms will bring up a new window showing the term's position in the Gene Ontology hierarchy, represented in tree form.
Interaction Type Result columns
A separate column will appear in the Selected Markers display for each interaction type, e.g. "Protein-DNA" selected in the Preferences tab. The numbers in the columns indicate, for each marker, the number of interactions returned by the query.
The number of interactions can be adjusted by changing the acceptance threshold using the throttle graph slider control.
Preferences
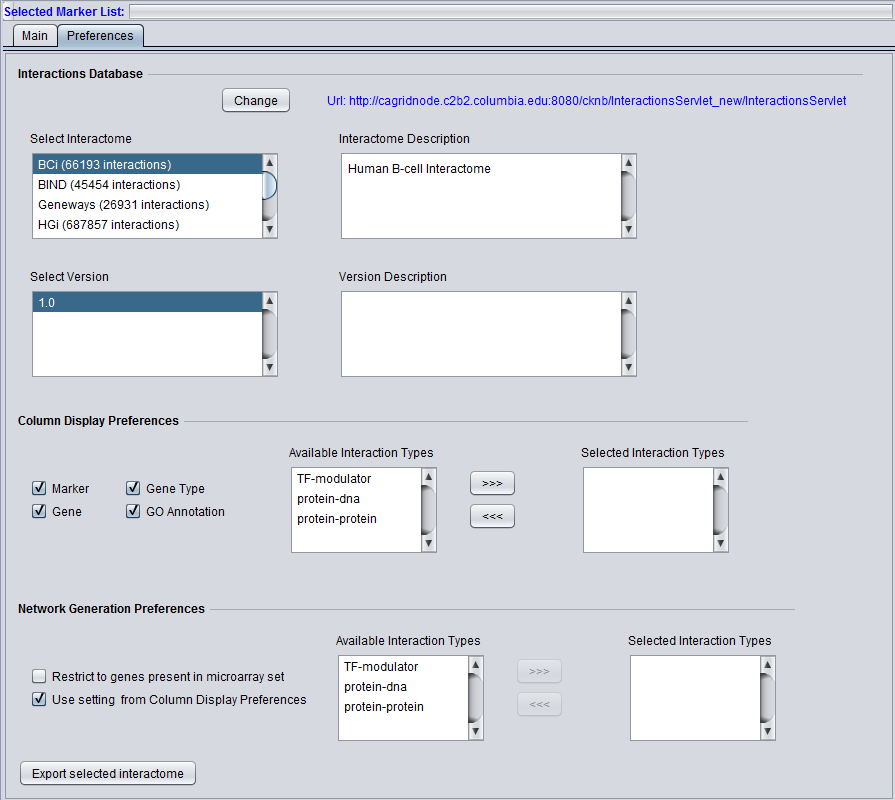
Interactions Database
The preferences panel shows a description (if available) of the chosen interactome, and in a separate pane a description (if available) of the interactome version.
Select CNKB instance
Change - This button allows the address at which to connect to the CNKB servlet to be changed. This should not normally be necessary.
Select Interactome
A list of all interactomes available in the CNKB is presented. The number of interactions present in each is shown in parantheses after the name. See also the CNKB data sources page.
Interactome Description
When an interatome is highlighted, its description, if available, will be presented in this window.
Select Version
An interactome may have multiple versions or releases. Each available version of the selected interactome will be presented here.
Some versions of an interactome may not yet be public. If so, the version number will appear in red, indicating that it is password protected.
Version Description
If available, a description of the selected version is displayed here.
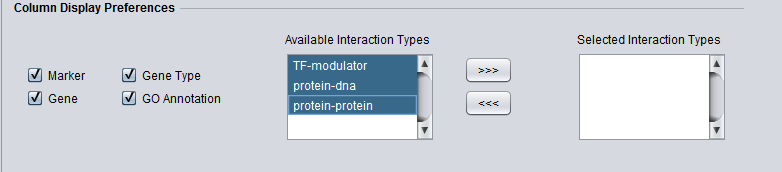
Column Display Preferences
These selections control which data columns will be displayed in the main "Selected Markers" pane.
- Marker
- Gene
- Gene Type
- GO Annotation
- Available Interaction Types - Contains a list of all interaction types used in the CNKB component that have not been already moved to the "Selected Interaction Types" list to the right. Note that this list is not specific to the particular data source chosen.
- Selected Interaction Types - A column in the Main tab "Selected Marker List" will appear for each interaction type appearing in this list.
List entries can be moved between the "Available" and "Selected" lists by either double-clicking directly on an entry, or through use of the right and left triple arrows "<<<", ">>>" located between them.
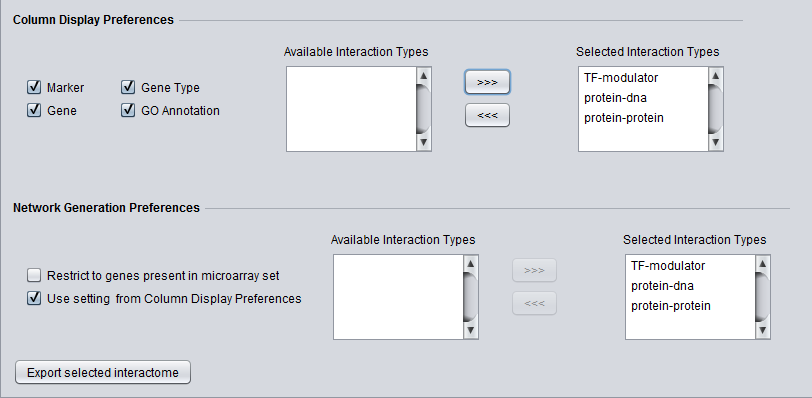
Network Generation Preferences
This section controls how the interactions returned by the database query will be used in creating a network. It allows, if desired, separate control of query and display.
- Restrict to genes present in microarray set - queries to the CNKB database may return interaction partners that are not members of the microarray dataset from which the original query markers were chosen. Checking this box will cause such markers NOT to be used in generating a network graph.
- Use setting from column display preferences
- If checked, the same interaction types that have been selected in the "Column Display Preferences" control above will be used in generating the network graph.
- If unchecked, only those interaction types added to the "Selected Interaction Types" list will be used to construct a network graph.
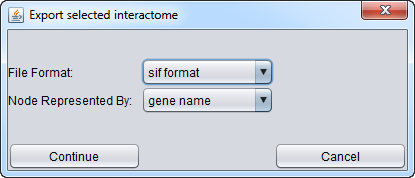
Export Interactome
The chosen interactions can be exported to a file on disk.
File Format
The interactions can be exported in either of two formats, SIF or ADJ.
SIF format
ADJ format
Node Identifier
- Gene Name - If available, the standard gene name associated with the gene id.
- Gene ID - the specific gene id that was used to represent the interactor in the original data. Depending on the type of interaction, the identifiers used may be the EntrezID, a miRBase or others.
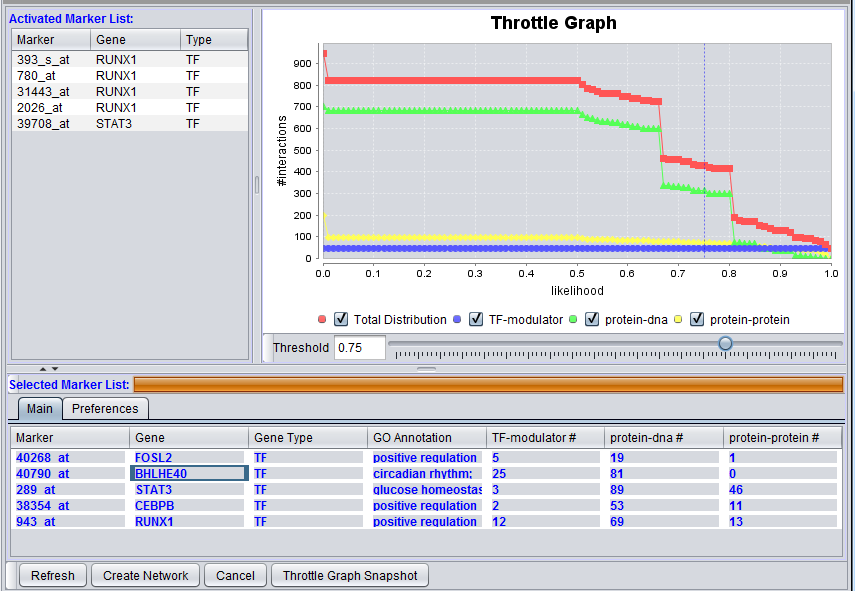
Throttle Graph
This interactive graph allows users to "throttle" (for the genes in the Selected Markers table) which interactions to work with, using as a criterion the interactions’ likelihood indicator. As the required threshold of likelihood of the interactions is increased, the number of interactions meeting this criterion decreases, as displayed in the query results columns (e.g "Protein-DNA") of the Selected Markers list.
The graph shows the result of querying on three interaction types. A fourth line depicts the sum of those three.
Check-boxes have been added to the display to allow individual interactions types to be turn on or off in the display.
Below, the likelihood cutoff is set to a value of 0.75.
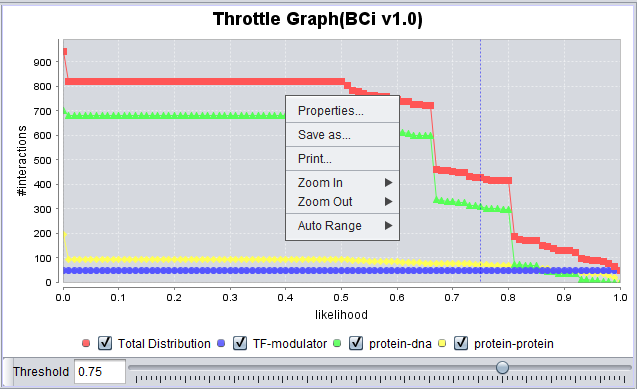
- Right-click menu - Right-clicking on the Throttle Graph will bring up a menu which allows the graph to be customized.
- Properties -
- Save as -
- Print -
- Zoom in -
- Zoom out -
- Auto Range - return to an automatically calculated range e.g. after use of Zoom function.
Example - Creating an interaction network and viewing it in Cytoscape
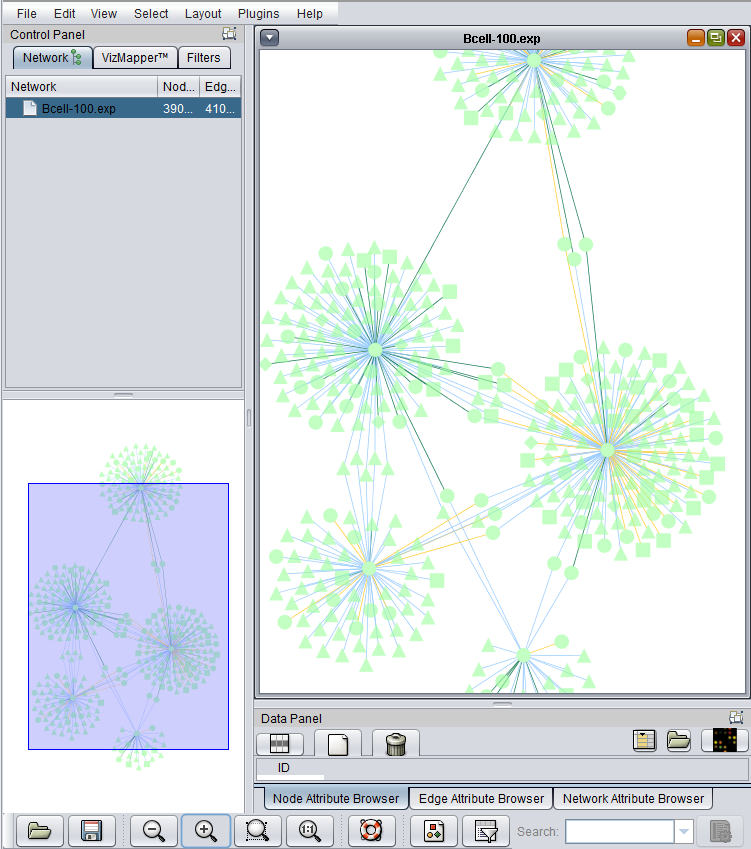
Once the desired set of markers is present and its interaction data has been retrieved from the database, an adjacency matrix can be computed by clicking the "Create Network" button. The resulting matrix is placed in the Project Folders component under its parent microarray dataset. The adjacency matrix is visualized in the Cytoscape Viewer.
Please note that if the targets retrieved from the Knowledge Base include markers/genes not present in the active microarray dataset, then whether those markers will be used in creating the network graph in Cytoscape is determined by the setting of the "Restrict to genes present in microarray set" checkbox under "Network Generation Preferences" on the CNKB Preferences tab.
The Cytoscape Viewer maintains a list of networks which it has currently loaded. It allows individual loaded networks to be deleted. However, the network can be reloaded by clicking on its entry in the Project Folders component. Cytoscape controls are more fully described in the Cytoscape component tutorial.
This example will briefly recapitulate the steps used in creating the figures shown in the above sections.
Prerequisites
- Data File: This example uses the Bcell-100.exp dataset available in the data/public_data directory of geWorkbench, and further described on the Download page. Briefly, this dataset is composed of 100 Affymetrix HG-U95Av2 arrays on which various B-cell lines, both normal and cancerous, were analyzed. Thus it explores a potentially wide variety of expression phenotypes.
- Annotation File: Obtain the annotation file for the HG-U95Av2 array type from the Affymetrix NetAffx website (http://www.affymetrix.com/analysis/index.affx). The name will be similar to "HG_U95Av2.na30.annot.csv", where "na31" is the version number. Loading the annotation file associates gene names and Gene Ontology information with the Affymetrix probeset IDs (see the geWorkbench FAQ for details on obtaining these files).
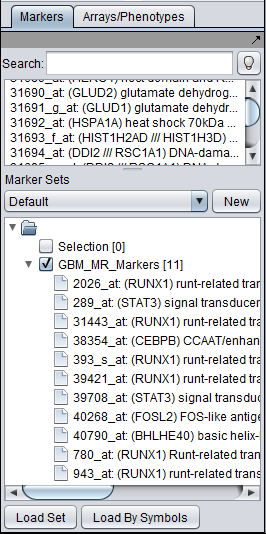
- Marker List: The list of markers used in this example is available in the file GBM_MR_Markers.
Loading the example data
- Load the Bcell-100.exp dataset into geWorkbench as type "Affymetrix File Matrix". (See Local Data Files).
- When prompted, load the annotation file.
- Create and activate a set of markers in the Markers component. For this example, save the file GBM_MR_Markers to disk and then load it directly into the Markers component by pushing its "Load Set" button and browsing to the file located in the geWorkbench directory data/public_data.
When the set is activated by checking the box to the left of its name, the transcription factor markers will appear in the "Activated Markers" list in the CNKB component.
Setting up the query in the CNKB component
(The steps shown below are also depicted in the screenshots for the individual control descriptions above).
1. In the "Activated Markers List", select (highlight) one marker for each gene. Choosing more than one marker per gene will just cause duplicates to appear in the query results display. Right-click on the "Activated Markers" list choose "Add Selected Markers to Selected Markers List". They will appear in the list in the "Main" tab of the Selected Markers list.
2. In the "Preferences" tab under Selected Markers choose the desired data source, version and interaction types.
- Select HGi_TCGA.
- Chose version 1.0 in the pulldown to the right.
- Select all three interaction types.
3. Return to the "Main' tab and hit the "Refresh" button. This will perform the query against the Cellular Networks Knowledge Base database.
4. Adjust the Throttle Graph to set a minimum likelihood requirement on interactions that will be used to create a network. Here, a value of 0.75 was used.
Note how the number of reported interactions decreases as the threshold is increased.
5. Hit the "Create Network" button.
6. The resulting adjacency matrix is displayed in the Cytoscape component in geWorkbench.
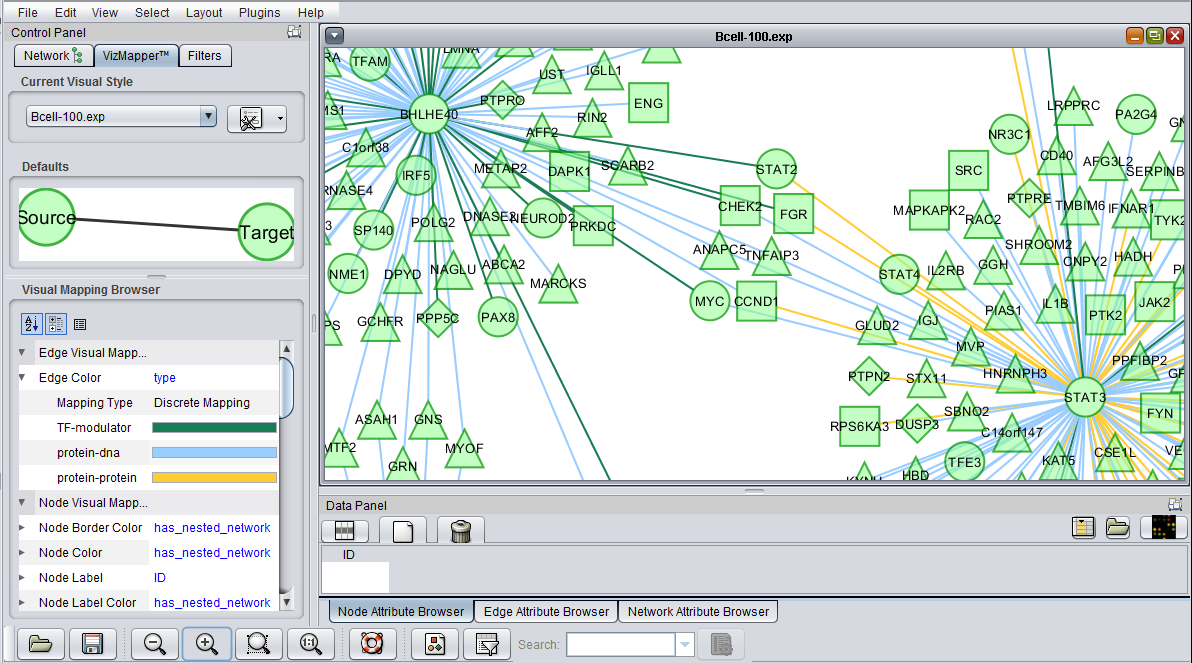
The edges are colored by the interaction type, e.g. Protein-DNA etc.
After enlarging the image, three node shapes can be seen, as well as the edges colored by the interaction types.
7. See the Cytoscape_Network_Viewer section for complete details on the many options available for working with this network.
Enhancements coming in geWorkbench v2.2
A number of enhancements have been made to the CNKB component. These enhancements have been completed in the development version of geWorkbench, and will be included in the next major release, which will be version 2.2.0 (expected by mid 2011).
As the additions to the functionality are quite interesting and useful, they are described here pre-release. Testing of the new features is ongoing, so they should be regarded as beta-release quality only.
Appendix - Data Sources
Please see the CNKB data page for a list of currently available data sources and types of interactions.
References
- Mani KM, Lefebvre C, Wang K, Lim WK, Basso K, Dalla-Favera R, Califano A., " A systems biology approach to prediction of oncogenes and molecular perturbation targets in B-cell lymphomas", Molecular Systems Biology 4:169, 2008. link to paper