Array Sets
Contents
- 1 Overview of Marker and Array Sets
- 2 Common Principles of Operation of Marker and Array Sets
- 3 Controls
- 4 Examples
- 4.1 Using the default Selection set
- 4.2 Assigning arrays to an new or existing set
- 4.3 Adding arrays to an existing set - shortcut
- 4.4 Removing an array from a set
- 4.5 Manipulating array sets
- 4.6 Activating sets
- 4.7 Classifying a set
- 4.8 Creating a new list to contain sets
- 4.9 Example of working with multiple array sets
Overview of Marker and Array Sets
The Markers/Arrays component, located at lower left in the geWorkbench graphical interface, allows the user to define and use sets of arrays and markers for a number of purposes.
As used in geWorkbench, the term "marker" includes genes, probes/probesets, and individual sequences, depending on the type of data loaded. Sets of markers can be returned by various analysis routines. For example, the t-test returns a list of markers showing significant differential expression, and after hierarchical clustering, the markers in a subtree of the resulting dendrogram can be saved to a list.
Sets of microarrays can be used to group arrays in a meaningful fashion for statistical analysis. For example, two such phenotypes might be the diseased and normal states of a tissue from which samples have been taken. geWorkbench uses the terms "Case" and "Control" to categorize these, but in biological setting the equivalent would be "Experimental" vs "Control".
This chapter discusses the use of sets of microarrays. Please see the chapter Data Subsets - Markers for a discussion of the use of Marker sets.
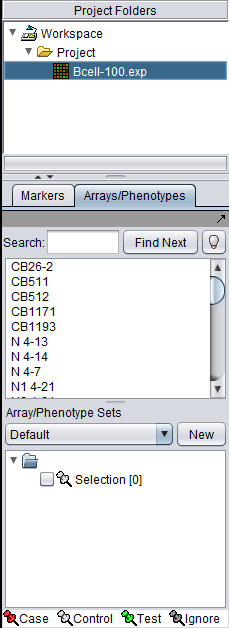
The figure below shows the Arrays/Phenotypes component located below the Project Folders component in geWorkbench. The Markers component is located in the same space, under a separate tab.
Common Principles of Operation of Marker and Array Sets
Rather than using all arrays or all markers in a data set for a particular analysis or visualization, the user may wish to restrict those used to only some subset.
Activating Sets of Markers and Arrays
In the Markers and Arrays components, sets of markers and arrays can be defined by the user, and also are created as the outcome of various analysis methods. Adjacent to each set in the graphical interface is a checkbox. Marking this box "checked" activates the subset.
- Activating a set restricts many geWorkbench components to using as input only the markers or arrays that are in such activated sets.
- Marker Sets
- If no Marker set is active, all Markers are used.
- If at least one Marker set is activated, affected components will only use markers that are in activated sets.
- Array Sets
- If no Array set is active, all Arrays are used.
- If at least one Array set is activated, affected components will only use arrays that are in activated sets.
Number of members displayed
To the right of each marker or array set, the number of members in the set is given inside square brackets.
Controls
Upper Pane
The list in upper pane of the Arrays component shows the arrays loaded in the current data set.
The upper pane of the Arrays/Phenotypes component has the following controls:
- Search text field - Search for arrays by typing in a name or portion of a name. As one types, the first array matching the entry so far will be highlighted. In some cases however, the Find Next button must be pushed to find a match. If the typed entry matches no arrays, it will be displayed in red.
- Find Next button - find the next array matching the typed entry.
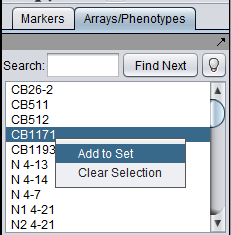
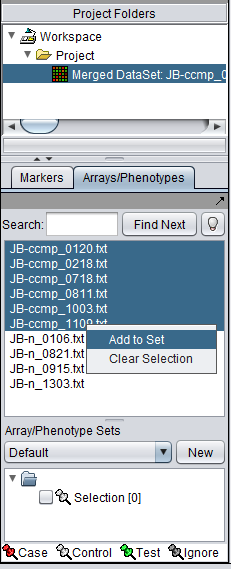
Selecting one or more arrays in the list and then right-clicking gives the following choices in a pop-up menu:
- Add to Set - Add the selected arrays to a new or existing subset.
- Clear Selection - unhighlights the selected arrays.
Lower Pane
The lower pane of the Arrays/Phenotypes component has the following controls:
- Array/Phenotype Sets menu - Select which named list of array sets to display. Each list can contain a different arrangement of the arrays into sets.
Note - The "Affymetrix Matrix File" microarray data file format, native to geWorkbench, supports multiple such lists being defined and saved.
- New button - Create a new list for array sets.
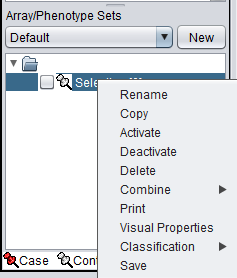
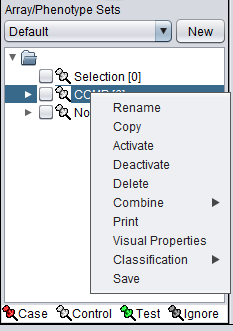
If you right-click on a subset, a menu with the following choices appears:
- Rename - Rename the selected set.
- Copy - Make a copy of the selected set.
- Activate - Activate the selected set. This can also be done directly by checking the check box before its entry.
- Deactivate - Deactivate the selected set. This can also be done directly by unchecking the check box before its entry.
- Delete - Delete the selected set.
- Combine - Combine the selected sets into a new set. Methods are:
- Union - Add all arrays from all selected sets.
- Intersection - Add arrays that are in each selected set.
- XOR - Add arrays that are in only one of the selected sets.
- Print - Print the selected set of arrays.
- Visual Properties - Change the color and shape of points representing arrays in graphical components, e.g. in the Scatter Plot.
- Classification - Designate the experimental class of an array set, chosen from: Case, Control, Test and Ignore.
- Save - Save the chosen set of arrays as a simple list (CSV format, one array per line) to a file on disk.
Examples
In this tutorial we will start with the same data files that were used in the Local Data Files tutorial. Load the ten individual MAS5 data files as shown there in the section "Loading microarray data files - local".
Using the default Selection set
Adding an array
Double clicking on an array in the upper list will add it to the default "Selection" set in the lower pane.
Removing an array
Double-clicking on the upper list entry again will remove an array from the default "Selection" set. More generally, for any array in the "Selection" set, double-clicking on its entry in the upper list will remove it from the set.
Assigning arrays to an new or existing set
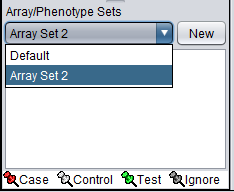
We will place the new sets of arrays in the "Default" list, however you can create a new list by pushing the New button on Array/Phenotype Sets at lower left.
First, we will select and label arrays which contain samples from the congestive cardiomyopathy disease state:
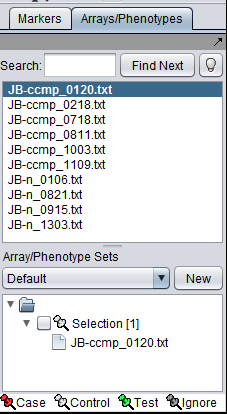
1. In the Arrays/Phenotypes component, select the six arrays beginning with JB-ccmp, which represent the samples from the congestive cardiomyopathy disease state.
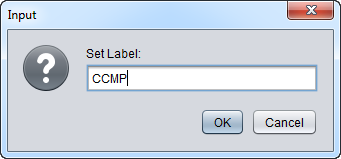
2. Right-click, select Add to Set. In the dialog box, you can enter the name of either an existing set, or of a new set to be created.
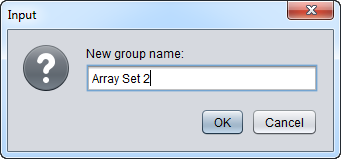
3. Enter the new subset name "CCMP" in the input box and click OK.
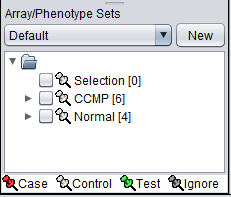
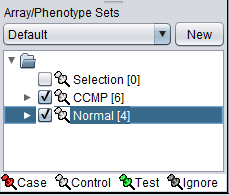
4. Next, similarly label the arrays beginning with JB-n as "Normal" ( repeat steps 2 & 3 ):
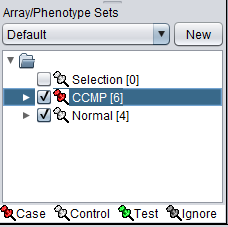
The Array/Phenotype Sets component will now show the two sets added:
Adding arrays to an existing set - shortcut
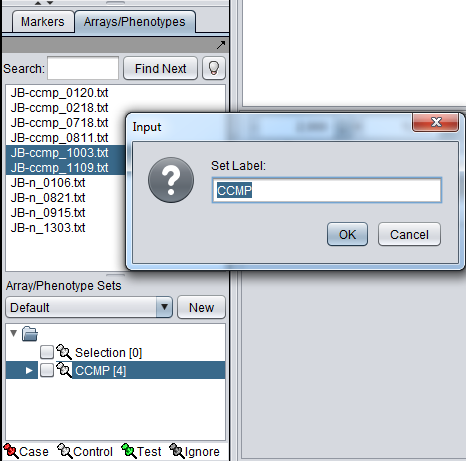
If you wish to add additional arrays to an existing set, you can avoid having to type in its name again in the dialog box by first selecting the target subset in the lower pane. Then right-click on a selection of arrays above and select "Add to Set" from the pop-up menu. The name of the existing set will appear in the "Add to Set" dialog.
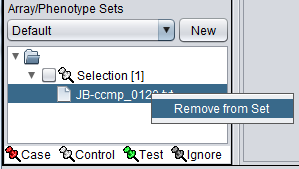
Removing an array from a set
One or more arrays can be removed from a set by highlighting them and the right-clicking. A menu will appear with option "Remove from Set".
Manipulating array sets
Right-clicking on an array set produces a menu with actions that can be applied to it, as already described in the Controls section. A few will be demonstrated in more detail in the following sections.
Activating sets
The check box next to a set name can be checked to "activate" a set. "Active". The use of activated sets has already been described above.
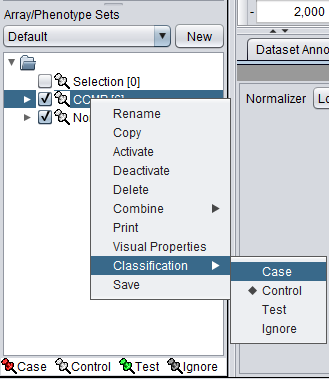
Classifying a set
For statistical tests such as the t-test, "Case" and "Control" sets can be specified.
- Left-click on the thumb-tack icon in front of the phenotype name.
- Select a classification, choosing from "Case", "Control", "Test", and "Ignore". The default classification is "Control".
A red thumbtack indicates the arrays have been specified as "Case".
Creating a new list to contain sets
Pushing the "New" button will bring up a dialog box in which the name of a new list can be entered.
In turn, once the new list is created, a new collection of sets can be created within it.
Example of working with multiple array sets
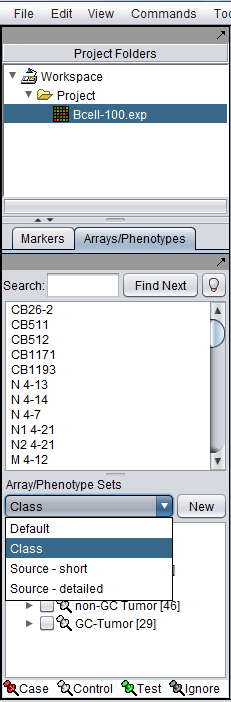
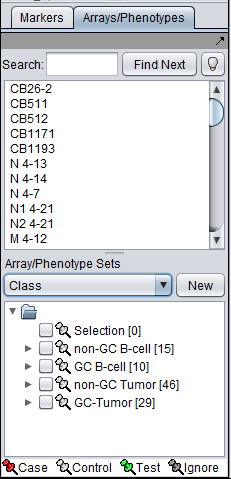
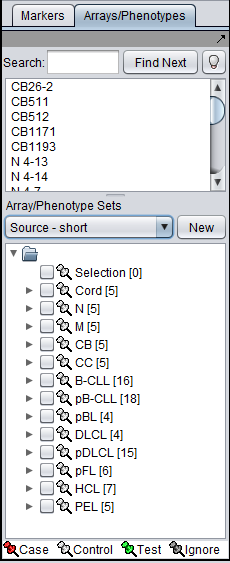
There can be different groupings of the same arrays in the Arrays/Phenotypes and Marker components. Here we show how there are several different lists of sets predefined in the example data file "BCell-100.exp". After loading this file into geWorkbench as type "Affymetrix File Matrix", the following lists of sets can be seen in the Arrays/Phenotypes group pulldown menu.
- Default
- Class
- Source- short
- Source - detailed
Each such list can contain a different arrangement of the arrays into subsets.
If we choose the list called "Class", the following sets of arrays are displayed:
If instead we choose the list "Source - short", a different division into subsets of the same arrays is seen: