BLAST
Contents
TUTORIAL - BLAST
In this Tutorial you will learn to:
- Set up and perform a Blast search.
- Decipher the Output.
- Analyze the results.
OVERVIEW
The BLAST algorithms are used to find similarities between a nucelotide or amino acid query seqeunce and sequences held in a database. They are often used to give clues to the function of a sequence based on its similarity to already characterized sequences.
geWorkbench runs BLAST by submitting jobs to remote BLAST services. The default is to send the job to a dedicated 40 CPU cluster operated by Joint Centers for Systems Biology at Columbia University. Its databases are updated on a weekly schedule by downloads from NCBI. geWorkbench can also submit jobs directly to the NCBI BLAST service. There is no provision at this time for running a local BLAST job on the client desktop machine.
Query files
BLAST accepts nucleotide or amino-acid query sequences in the FASTA format. A query file can contain one or multiple sequences. The file can be loaded from disk using the File Open command, or may have been placed into the project by components such as the Sequence Retriever, or as a result of a previous BLAST run.
Databases
Both remote BLAST services provide a number of databases of both nucleic acid and protein sequences.
Searching using translated sequences
If desired, the algorithms allow either a nucleotide query, a nucleotide database, or both to be translated into amino-acid sequence. Searching in the amino-acid space is more sensitive for certain types of query, as it ignores synonymous, non-functional changes in nucleotide sequence.
Algorithms
There are five different query programs one can run:
blastp- Compares an amino acid query sequence against a protein sequence database.
blastn- Compares a nucleotide query sequence against a nucleotide sequence database.
blastx- Compares a nucleotide query sequence translated in all reading frames against a protein sequence database.
tblastn- Compares a protein query sequence against a nucleotide database dynamically translated in all reading frames.
tblastx- Compares the 6 frame translations of a nucleotide query sequence against the six frame translations of a nucleotide sequence database. This last is needless to say very time consuming!
Example
Two Genbank Fasta sequence files are provided in the tutorial dataset, a nucleotide sequence, "NM _024426-Wilms.Fasta", and its protein sequence, "NP_077744-Wilms.fasta".
For a simple search using the nucleotide query file, one can select the blastn program and search against the ncbi/nt non-redundant database of nucleotide sequences. For an even quicker example search, one could run the protein query sequence against a small protein database derived from those sequences found in the PDB database of proteins having known structures.
Here we will illustrate a search using the nucleotide file "NM _024426-Wilms.Fasta".
- Read the "NM _024426-Wilms.Fasta" data file into the Project component using the File Open command and file type FASTA.
- In the Project component, make sure the sequence file just read in is selected. This will activate those components that can work with sequence data.
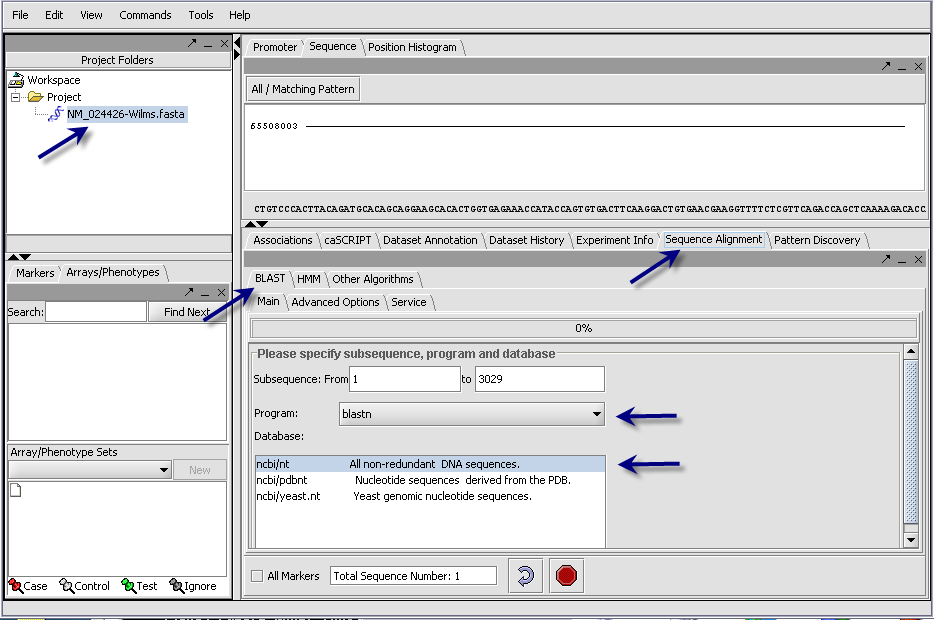
- In the Commands Area click on the Sequence Alignment tab.
- Select the Blast tab.
The length of the sequence is shown, and if desired a subset of the input sequence can be specified for use in the search. In the case where more than one sequence was read in, the length of the longest is displayed.
- Click on the drop down arrow and select a program. Since this is a nucelotide query, here we select a nucleotide query program blastn.
- Select the desired nucleotide database. Here select ncbi/nt - the complete non-redundant nucleotide database. For a faster search, one could select the ncbi/pdbnt database instead, which is much smaller.
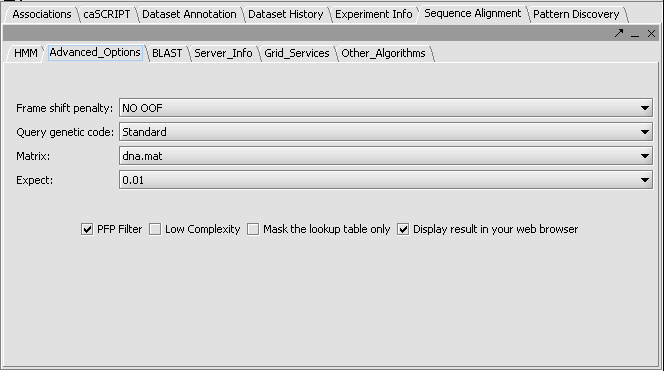
- Click on the Advanced Options Tab
- Make sure "dna mat" is selected for the Matrix.
- Change the Expect Value to 0.01. This sets the cutoff for which BLAST hits will be displayed.
- Leave the box checked for PFP filtering for repeated sequence elements (Paracel Filtering Package).
- Leave the Display result in your web browser checked.
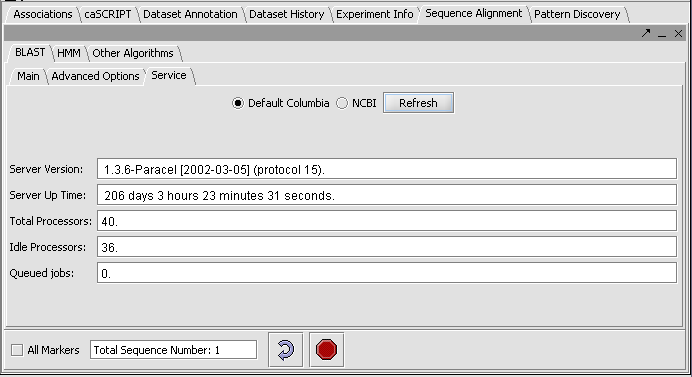
- Click on the Service tab. By default, jobs will be submitted to the BLAST server at Columbia. This server runs Paracel BLAST and is optimized for large searches, for example jobs where the query contains hundreds or thousands of input sequences. You can also select the BLAST server at NCBI. This has the advantage of providing access to the latest version of NCBI BLAST.
Note: The text field at the bottom shows that one sequence has been selected. If you have a Fasta file that has multiple sequences, you can select the ones you want in the Markers component and activate this selection, letting you search on a subset. You may search on all sequences in a file by clicking the All Markers checkbox.
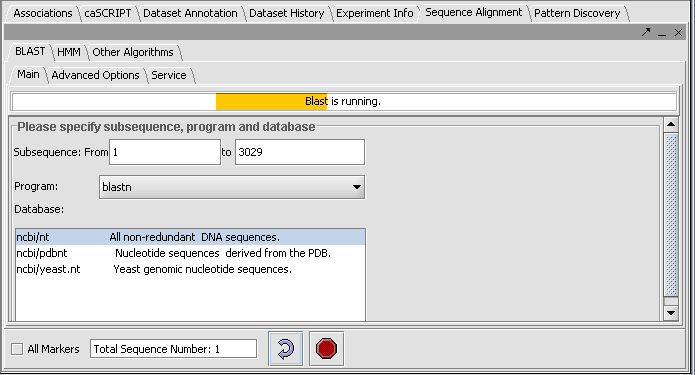
- Press the curved arrow submit button.
- Observe the progress bar, it will show that Blast is now runnning.
- You can check the server status by hitting the Refresh button under the Service tab. This will show the load and backlog on the Columbia server. However, the server uses a scheduling method that allows small queries to slip through past long-running queries as nodes become available.
When the results are returned they are placed in the Project Folders as a child of the sequence they correspond to. You can mouse over the result set to see how many sequences are in it.
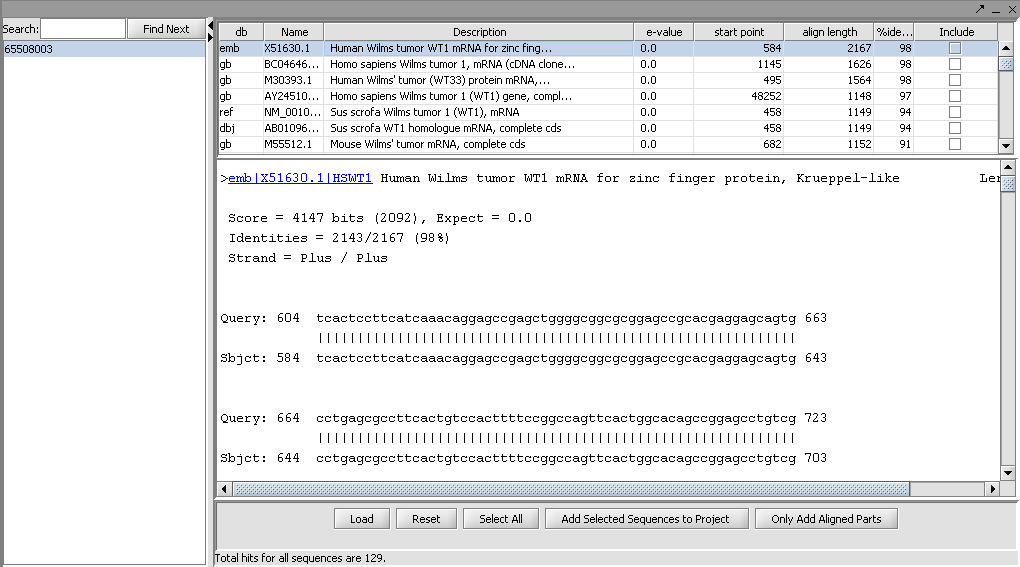
The result file will be opened in your web browser, if this option was selected. The alignment results are also displayed directly in the geWorkbench Blast results viewer and can be there further manipulated. Each different target hit is listed on a line in the results table. Note that a query sequence can hit a database target sequence in more than one place, resulting in mulitple alignments displayed per target hit.
In the Blast results viewer you can select sequences to add back to the main project by checking the include box and then the Add Selected Sequences To Your Project button.
You can also add just the aligned parts by clicking on the button Only Add Aligned Parts.
The results viewer also shows statisics for each hit, including the E-value, start and length of the hit, and the percent identity.
In the Blast results viewer, the Load button allows one to load an external Blast file in HTML format into the viewer.