BLAST
Contents
Overview
This section describes the functionality present in geWorkbench 2.1.0. With release 2.1.0, geWorkbench supports almost all BLAST setting options available through the NCBI web interface.
The BLAST algorithm is found in the Sequence Alignment tab, located in the command area of geWorkbench (lower right quadrant). The Sequence Alignment tab appears when a protein or DNA sequence is loaded and selected in the Project Folders component. BLAST is currently the only alignment option supported in the Sequence Alignment component.
The BLAST algorithm is used to find similarities between nucleotide or amino acid query sequences and sequences held in a database. It is often used to give clues to the function of a sequence based on its similarity to already characterized sequences.
geWorkbench runs BLAST by submitting jobs to the NCBI server. NCBI-supported sequence databases and search algorithms can be selected in the user interface. There is no provision at this time for running a local BLAST job on the client desktop machine.
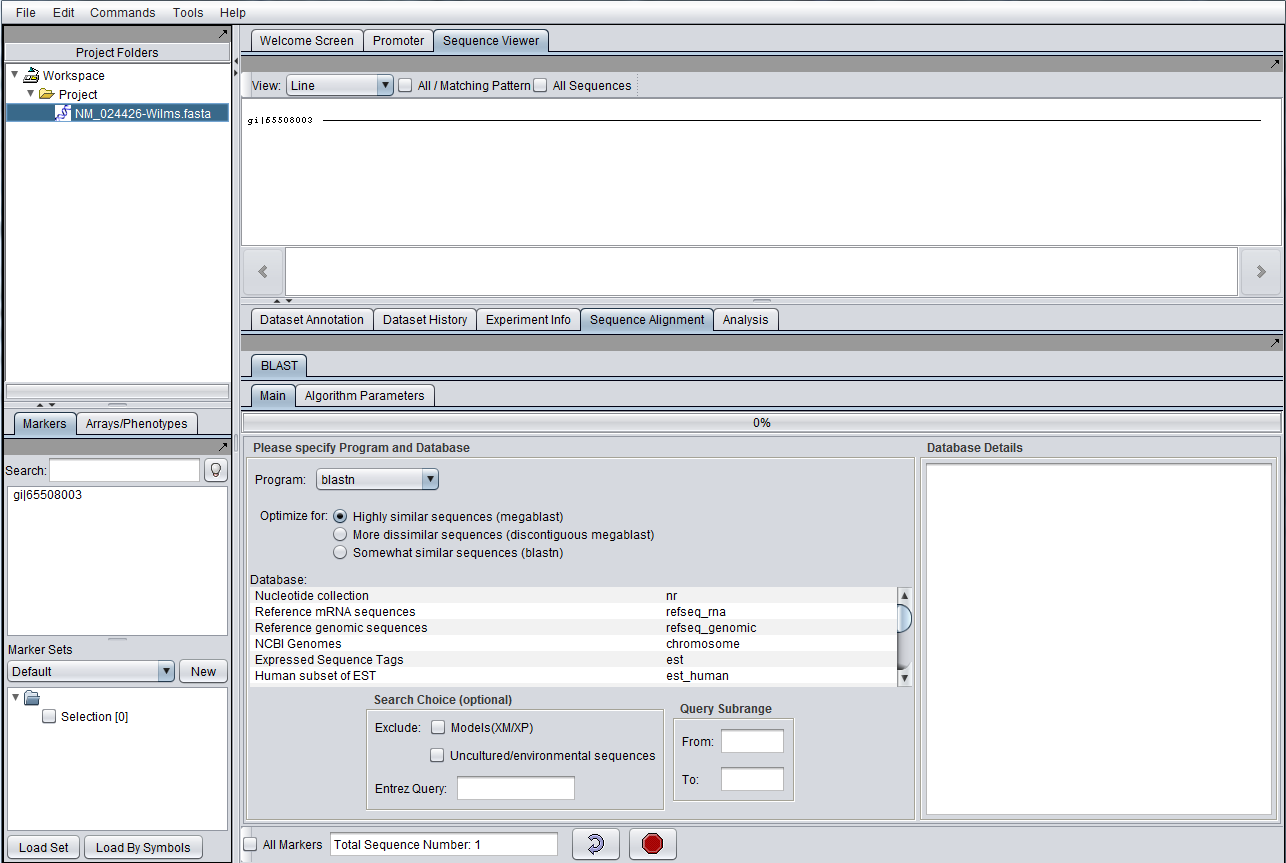
Figure legend: BLAST within the Sequence Alignment component. A nucleotide sequence has been loaded into the Project Folders component (upper left). The Sequence Viewer component displays this sequence (upper right). The Sequence Alignment/BLAST interface is shown at lower right.
BLAST job setup
Prerequisites
- The Sequence Alignment component must be loaded in the geWorkbench Component Configuration Manager.
- A protein or nucleotide sequence must be loaded in the Project Folders component.
Query sequences
BLAST accepts nucleotide or amino-acid query sequences in the FASTA format. A query file can contain one or multiple sequences. The file can be loaded from disk using the File Open command, or may have been placed into the Project Folders component by another component such as the Sequence Retriever, or as a result of a previous BLAST run.
NCBI Documentation
geWorkbench serves as a interface to the NCBI BLAST server and implements the same options as the NCBI BLAST website. Detailed information about each option can be found on NCBI webpages, including:
Older help pages...
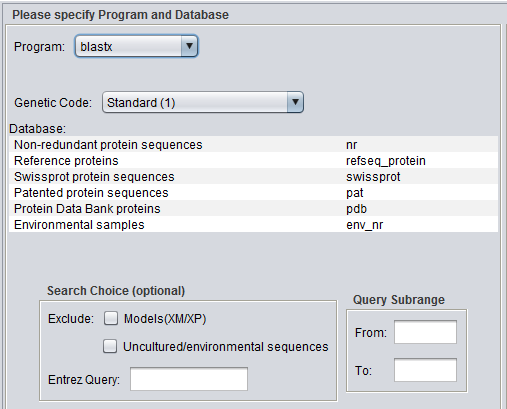
Parameters - Main
In addition to the parameters shown in the previous image, BLASTX and TBLASTX add the Genetic Code option:
Algorithms
The user must make sure that the algorithm chosen matches the type of query sequence (protein or nucleotide) that has been loaded. Some of the algorithms translate a nucleotide query, a nucleotide database, or both into amino acid sequence before executing the query. Searching in the amino-acid space is more sensitive for certain types of query, as it ignores synonymous, non-functional changes in nucleotide sequence.
For protein query sequences:
- blastp - Compares an amino acid query sequence against a protein sequence database.
- tblastn - Compares a amino acid query sequence against a nucleotide database translated in all reading frames.
For nucleotide query sequences:
- blastn - three algorithms are available under the blastn choice, in order of decreasing similarity of the query to the target sequences, Each compares a nucleotide query sequence against a nucleotide sequence database:
- megablast - for highly similar sequences.
- discontinuous megablast - for more dissimilar sequences
- blastn - for somewhat similar sequences.
- blastx - Compares a nucleotide query sequence translated in all reading frames against a protein sequence database.
- tblastx - Compares the 6-frame translations of a nucleotide query sequence against the 6-frame translations of a nucleotide sequence database.
Databases
Standard protein and nucleic acid databases maintained at NCBI are supported. The appropriate databases for the search algorithm chosen will be displayed. A window to the right, "Database Details", displays a summary of the database currently selected in the list.
For nucleic acids:
- Nucleotide Collection (nr/nt)
- Reference mRNA seqeunces (refseq_rna)
- Reference genomic sequneces (refseq_genomic
- NCBI Genomes (chromosome)
- Expressed Sequence Tags (est)
- Human subset of EST (est_human)
- Mouse subset of EST (est_mouse)
- Non-human, non-mouse ESTs (est_others)
- Genomic survey sequences (gss)
- High throughput genomic sequences (htgs)
- Patent sequences (pat)
- Protein Data Bank (pdb)
- Human ALU repeat elements (alu)
- Sequence tagges sites (dbsts)
- Whole genome shotgun reads (wgs)
- Environmental Samples (env_nt)
For proteins:
- Non-redundant protein sequences (nr)
- Reference proteins (refseq_protein)
- Swissprot protein sequences (swissprot)
- Patented protein sequences (pat)
- Protein Data Bank sequences (pdb)
- Environmental samples (env_nr)
Search Choice
These settings provide the ability to restrict the search in certain ways
- Exclude: exclude certain specialized database entries from the search.
- Models (XM/XP)
- Uncultured/environmental sequences
- Entrez Query - an Entrez format query can be entered directly to restrict a search e.g. to a particular species.
Genetic Code
Genetic code to be used in blastx (and tblastx) translation of the query.
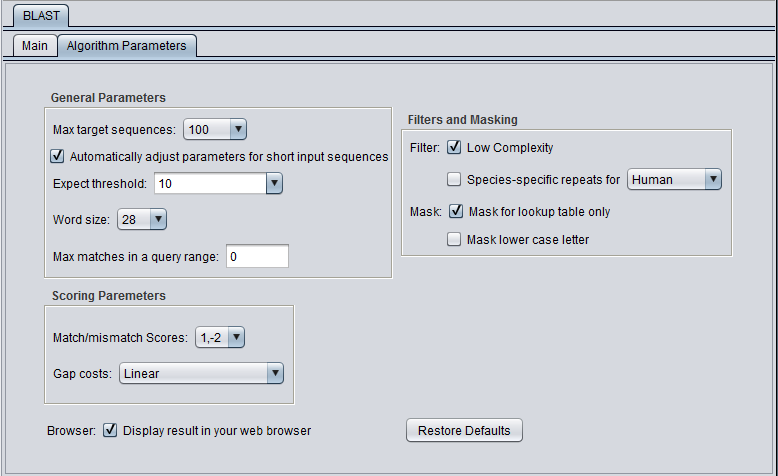
Parameters - Advanced Options
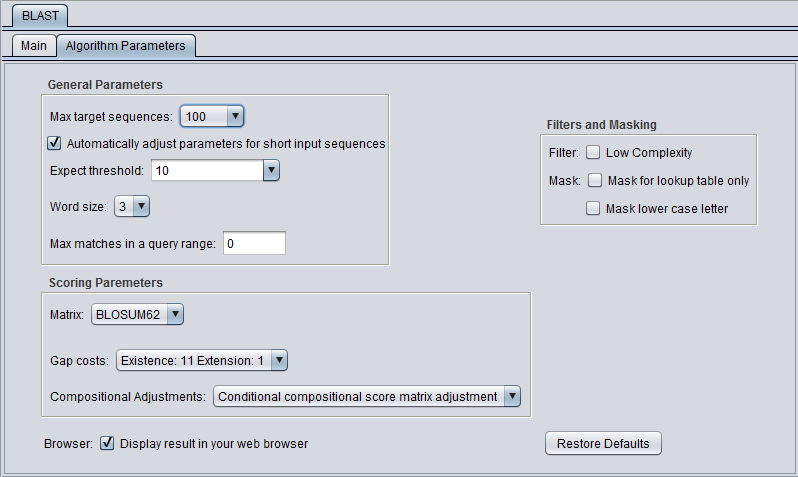
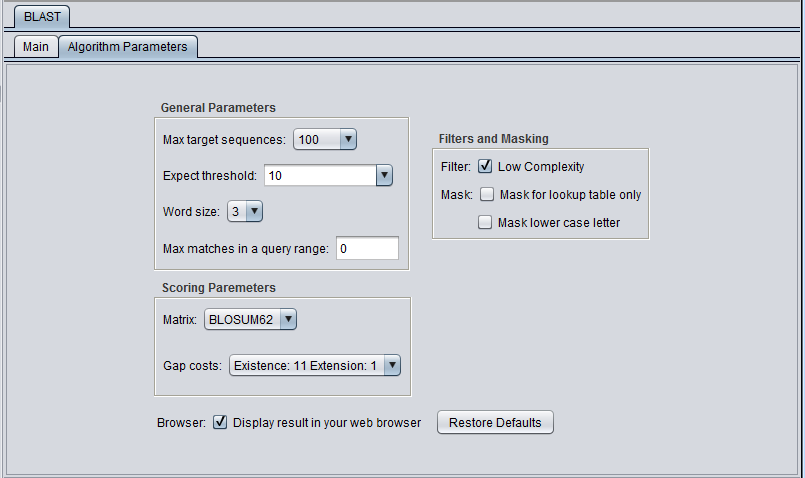
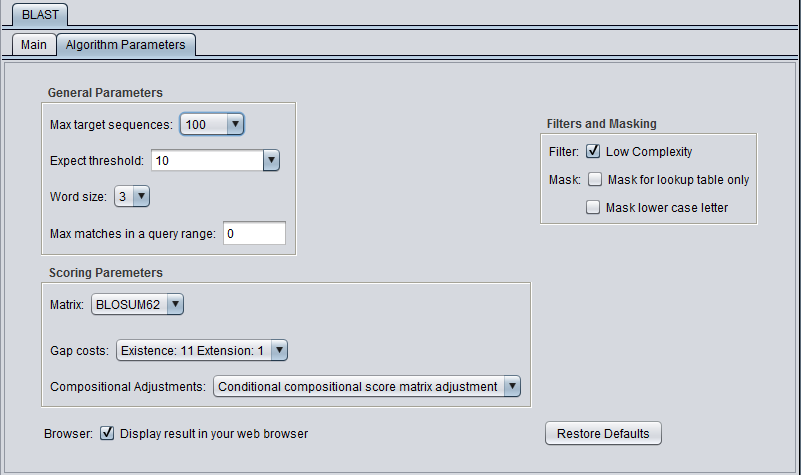
General Parameters
- Max target sequences - maximum number of hits to return.
- Automatically adjust parameters for short input sequences.
- Expect threshold - Expected number of chance matches in a random model.
- Word size - The length of the seed that initiates an alignment.
Scoring Parameters
- Match/mismatch scores (blastn, megablast, discontinuous megablast) - scores to use for a match or mismatch.
- Matrix - Various scoring matrices (BLOSUM, PAM) are available for protein and translated queries.
- Gap Costs - The pull-down menu shows the available choices of gap costs for the current scoring matrix.
- Compositional adjustments - "...takes into account the amino acid composition of the individual database sequences involved in reported alignments. This improves E-value accuracy, thereby reducing the number of false positive results."
Filters and Masking
- Low Complexity - filter out low compositional complexity sequence.
- Species-specific repeats filter - masks species-specific repeats (e.g. human LINE's and SINE's). This option can speed searches involving long query sequences or databases containing sequences with many repeats.
- Mask for lookup table only - masks low-complexity sequence only while constructing the lookup table used by the initial hit-find phase of BLAST. The second phase, hit extension, is not not affected and hits can be extended through low-complexity sequence. NCBI notes that this option is experimental and subject to change.
- Mask lower case letter - filter out sequence which is in lower case in the FASTA query sequence.
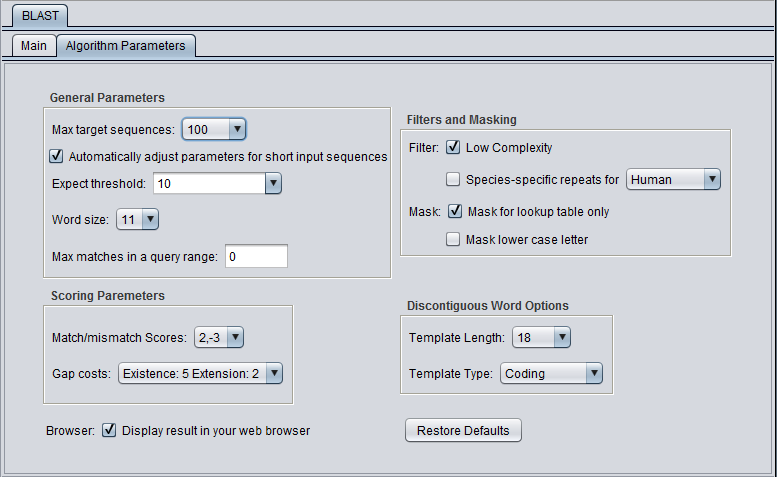
Discontiguous Word Options
- Template Length - None, 16, 18 (default), 21.
- Template Type - Coding (default), Maximal, Two Template.
Please see the NCBI page on discontiguous megablast for a detailed explanation of these options.
Other
- Display result in your web browser - geWorkbench will display the HTML page returned by NCBI BLAST in your web browser as well is within its own display.
- Restore defaults - restore all settings for the currently selected algorithm to their default values.
Advanced Parameter Setting Defaults
blastn and megablast
discontiguous megablast
blastp
blastx and tblastx
tblastn
General controls
- All Markers - if selected, use all sequences loaded, overriding any activated sets in the Marker Sets component.
- Total Sequence Number - indicates how many sequences have been selected for query.
- Curling arrow - start BLAST search
- Stop sign - stop BLAST search (if pushed, geWorkbench will not wait for or retrieve the BLAST results).
Submitting a BLAST job
- Press the curved arrow submit button. The adjacent Stop button will terminate the search (geWorkbench will not wait for or retrieve the BLAST results).
- Once the search has been submitted, a progress bar in the "Main" tab will indicate first that the sequence is being uploaded and then that the job is running.
BLAST Results Viewer
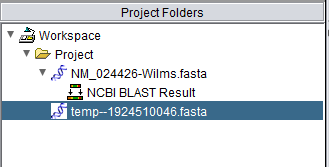
When the BLAST search results are returned they are placed in a new node in the Project Folders component as a child of the query sequence used. Mousing over the result set will show how many sequences are in it.
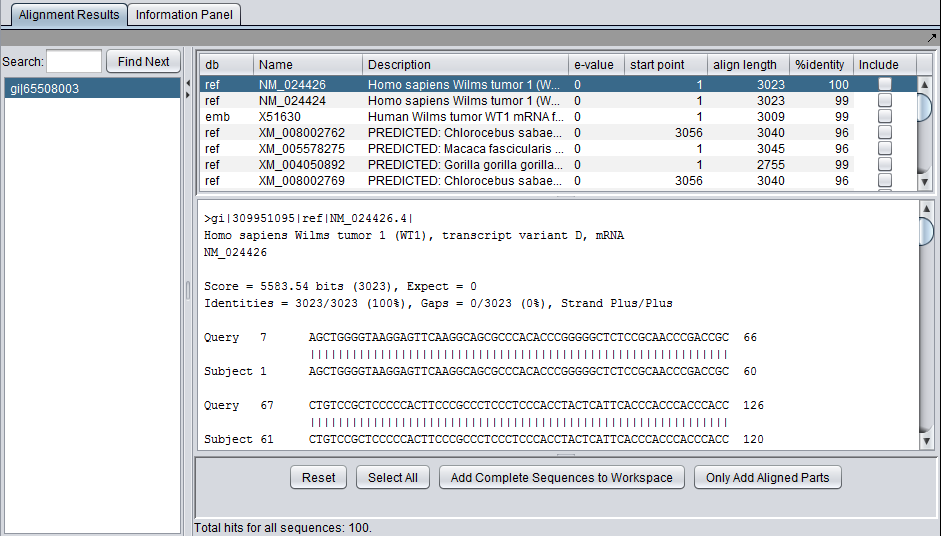
Each different hit is listed on a line in the results table, shown below. Note that a query sequence can hit a database target sequence in more than one place, resulting in multiple alignments displayed per target hit. The results viewer also shows statisics for each hit, including the E-value, start position and length of the hit, and the percent identity.
If the "Display result in your web browser" option was chosen, then the browser will open with the HTML formated results.
In the pane at left in the picture below, the name of the input query sequence is shown, e.g. the gi number of a Genbank sequence. If there had been more than one query sequence, then this pane would show a list of query sequence names, allowing you to select the results to be viewed.
Controls
Within the list of returned hits
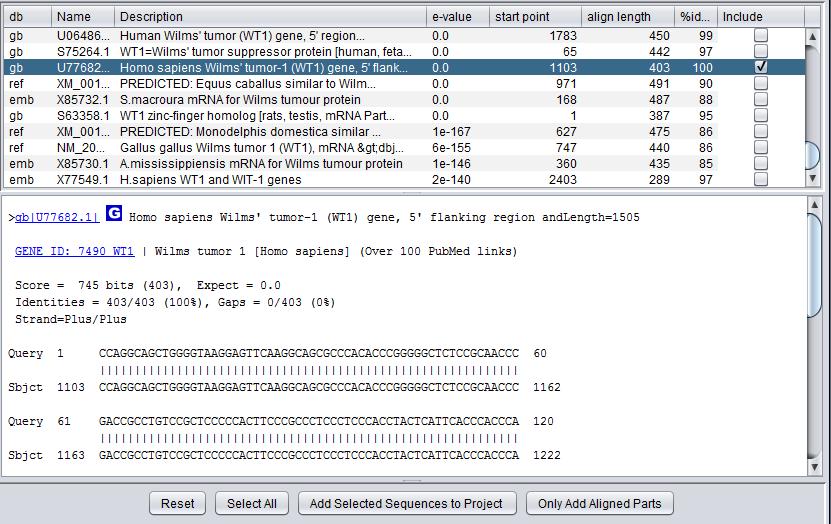
- Include check boxes - when checked, selects these sequences for import into the Project Folders component.
At the bottom of the pane
- Reset - uncheck all "Include" boxes.
- Select All - mark as checked all the "Include" boxes.
- Add Selected Sequences to Project - for each hit whose "Include" box is checked, add its sequence to a sequence node in the Project Folders component.
- Only Add Aligned Parts - for each hit whose "Include" box is checked, add to the Project Folders component only the portion of its sequence which aligned with the query sequence .
In the query list
- Search - input a text search to find entries in the list of queries.
- Find Next - search for the next occurence of the entered text.
Adding selected hit sequences to the project
The sequences corresponding to individual hits in the BLAST search can be retrieved from NCBI and added to the Project Folders component.
Here we select a particular hit, by checking the "include" box next to it, and press the button "Add Selected Sequences to Project". The sequence is retrieved and placed into the Project Folders component as shown below:
Example: Running a BLAST search
Two Genbank sequence files in FASTA format are included in the geWorkbench data/public_data folder: a nucleotide sequence, "NM _024426-Wilms.Fasta", and its protein sequence, "NP_077744-Wilms.fasta".
For a simple search using the nucleotide query file, one can select the blastn/megablast program and search against the nr/nt database of nucleotide sequences.
- From the geWorkbench "File" menu, select "Open->File".
- Select a file type of FASTA.
- Navigate to data/public_data within the geWorkbench distribution and select the file "NM _024426-Wilms.Fasta".
- Press "Open".
- (The above steps can also be accomplished by right-clicking on a Project node and selecting "Open File(s)" and following the same steps.
- In the Project Folders component, make sure the sequence file just read in is selected. This will activate those components that can work with sequence data.
- In the Commands Area click on the Sequence Alignment tab.
- Select the BLAST tab, and under it the Main tab.
- For program select blastn, and leave the default algorithm choice set to megablast.
- For database, select nr - the complete nucleotide database.
Note: The text field at the bottom of the Sequence Alignment component shows the number of sequences that have been selected. If you have a fasta file that has multiple sequences, you can select the ones you want in the Markers component and activate this selection, letting you search on a subset. You can override an activated Marker Set and search on all sequences in a file by clicking the All Markers checkbox.
- Click on the Advanced Options Tab
- Change the Expect Value to 0.01. This sets the cutoff for which BLAST hits will be displayed.
- Leave the Display result in your web browser checked.
- Hit the "curving arrow" run button. The job will be submitted and the results returned as shown in the sections above.