Difference between revisions of "Tutorial - GO Term Enrichment"
(→Example) |
(→Preparations) |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
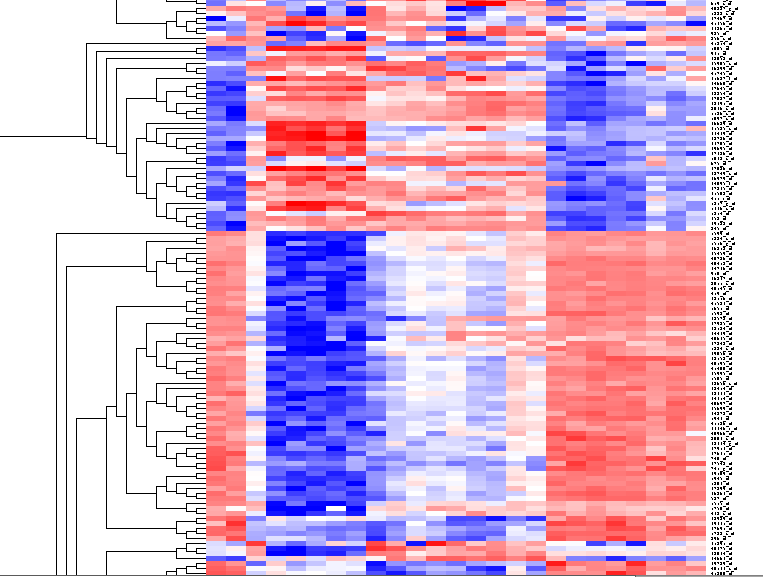
The results will be displayed in the Dendrogram component. | The results will be displayed in the Dendrogram component. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:T_HierarchicalClustering_BCregion.png]] | ||
| + | |||
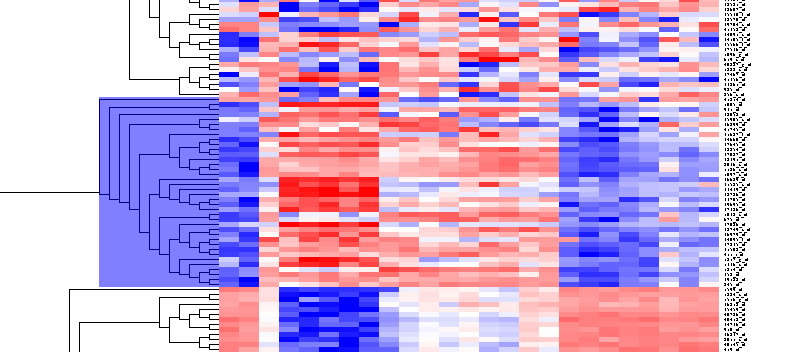
| + | By scrolling down a bit, one finds the first large interesting cluster, showing clear differences between groups of arrays. Check the '''Enable Zoom''' checkbox. Highlight the cluster as shown. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:T_HierarchicalClustering_BC38Markers.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then left-click to select this subset of the dendrogram. It will be displayed alone. | ||
| + | Now right-click and select "Add to Set". In the Markers component, the select genes are added as Cluster Tree [38], where 38 is the number of markers selected. | ||
Revision as of 18:05, 24 April 2006
Overview
The Gene Ontology component allows the exploration of the Gene Ontology (GO) terms represented within a list of genes. Several different display options are available. The entire GO can be displayed as a tree (TreeView), with the selected genes being shown within the tree. Or, the list of genes can be displayed sorted by their overrepresentation P-values (TableView). This P-value is calculated from the observed vs expected number of hits to a category based on its representation in markers annotated in the microarray type as a whole, e.g. HG_U95Av2.
Example
In this example we will use the file "webmatrix_quantile_log2_dev1_mv0.exp" available in the tutorial data section (coming soon).
Preparations
We must first obtain a list of interesting genes. We will use the results obtained in the tutorial on hierarchical clustering. In brief, this clustering result can be recreated by these steps:
- In the Arrays/Phenotypes component, select the set of arrays labeled "ultrashort designation".
- Activate two classes of arrays to compare, the GC B-cell and non-GC B-cell, by checking the boxes before the names.
- Go to the Analysis component, and select Hierarchical Clustering.
- At the bottom of the Analysis component, uncheck the box that says "All Arrays". This will allow the clustering to be done only on those arrays which were activated in the Arrays/Phenotypes component.
- In Hierarchical Clustering, set the parameters to:
- Clustering Method: Total Linkage
- Clustering Dimension: Both
- Clustering Metric: Euclidean
- Click Analyze.
The results will be displayed in the Dendrogram component.
By scrolling down a bit, one finds the first large interesting cluster, showing clear differences between groups of arrays. Check the Enable Zoom checkbox. Highlight the cluster as shown.
Then left-click to select this subset of the dendrogram. It will be displayed alone. Now right-click and select "Add to Set". In the Markers component, the select genes are added as Cluster Tree [38], where 38 is the number of markers selected.