Difference between revisions of "Tutorial - GO Term Enrichment"
(→Example) |
|||
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{TutorialsTopNav}} | {{TutorialsTopNav}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note - this component is not distributed as part of geWorkbench 1.6.* or latter versions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Outline== | ||
| + | In this tutorial we will | ||
| + | #. Investigate a set of genes chosen in the Hierarchical Clustering tutorial. | ||
| + | #. Generate a map of Gene Ontology (GO) terms matching the selected genes. | ||
| + | #. Use the table view to find which GO categories are most significantly overrepresented. | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
| Line 5: | Line 13: | ||
==Example== | ==Example== | ||
| − | In this example we will use the file " | + | In this example we will use a set of genes originating from the file "webmatrix_quantile_log2_dev1.2_mv0.exp" available in the tutorial data section. The list of 84 markers was obtained as shown in the Hierarchical Clustering tutorial. The marker list can also be directly loaded from the file cluster_tree_total_pearsons_84_markers.csv found in the tutorial data download. |
| + | |||
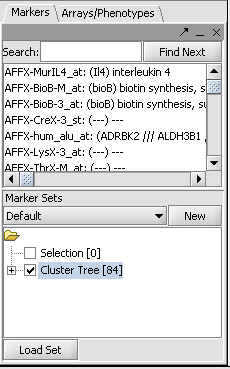
| + | * Activate the list by checking its box in the '''Markers''' component as shown: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Tutorial-Markers-ClusterTree84.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
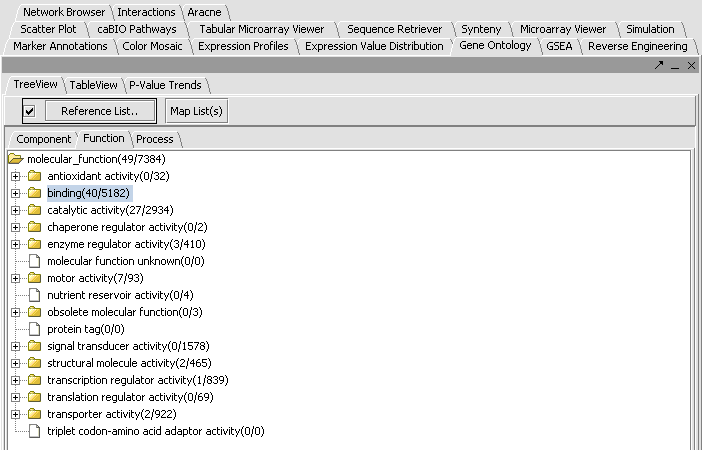
| + | * In the Gene Ontology component, choose the type of GO term that one wants, either '''Component''', '''Function''' or '''Process'''. In this example we will select the '''Function''' tab. | ||
| + | * Click on '''Map List(s)'''. | ||
| + | * We see in the picture below that 49 of the 84 total genes were placed in functional categories. By scrolling and by clicking on individual tree nodes, we can explore the tree. We see that the largest single category, with 40 hits, was binding. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Tutorial_GeneOntology_Result.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
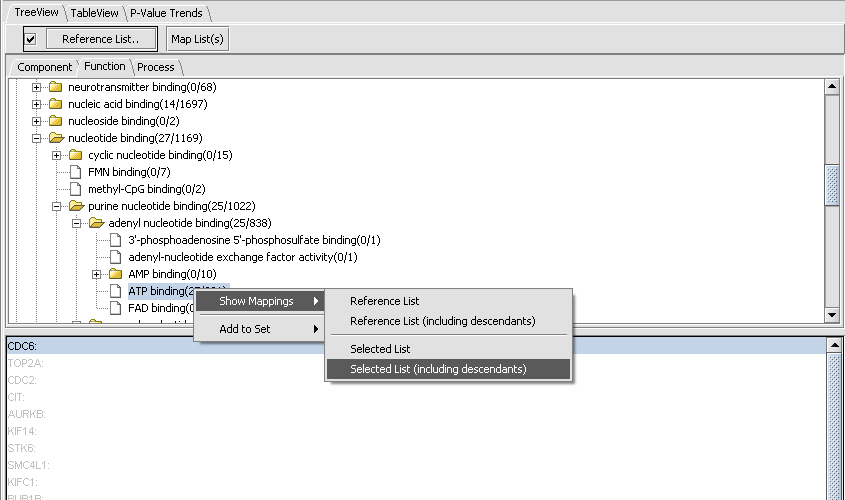
| + | By clicking on the binding node, we can travel down to increasing levels of detail. By right-clicking on a folder or file icon and selecting Show Mappings->Selected List(including descendents) as shown below, we can see the gene names of the genes categorized at or below that level, here 25 involved in ATP binding. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Tutorial_GeneOntology_Result-binding2.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
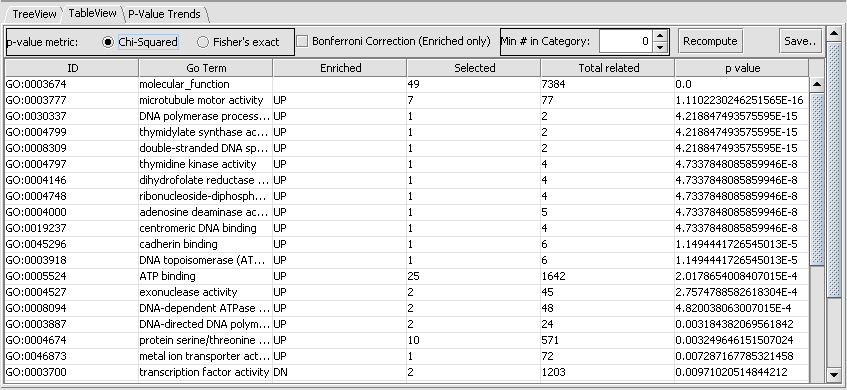
| + | A second view of the data is available by clicking on the TableView tab. This will show the degree of overrepresentation in GO categories. Here is the data for the Function category for the same list as above: | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | [[Image:Tutorial_GeneOntology_TableView.png]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Here we see that the category with most significant overrepresentation is "microtubule motor activity". | ||
| − | + | Note the Save button at right on the component. This will dump the entire contents of the table to a text file with extension .dat. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 16:26, 14 July 2009
Note - this component is not distributed as part of geWorkbench 1.6.* or latter versions.
Outline
In this tutorial we will
- . Investigate a set of genes chosen in the Hierarchical Clustering tutorial.
- . Generate a map of Gene Ontology (GO) terms matching the selected genes.
- . Use the table view to find which GO categories are most significantly overrepresented.
Overview
The Gene Ontology component allows the exploration of the Gene Ontology (GO) terms represented within a list of genes. Several different display options are available. The entire GO can be displayed as a tree (TreeView), with the selected genes being shown within the tree. Or, the list of genes can be displayed sorted by their overrepresentation P-values (TableView). This P-value is calculated from the observed vs expected number of hits to a category based on its representation in markers annotated in the microarray type as a whole, e.g. HG_U95Av2.
Example
In this example we will use a set of genes originating from the file "webmatrix_quantile_log2_dev1.2_mv0.exp" available in the tutorial data section. The list of 84 markers was obtained as shown in the Hierarchical Clustering tutorial. The marker list can also be directly loaded from the file cluster_tree_total_pearsons_84_markers.csv found in the tutorial data download.
- Activate the list by checking its box in the Markers component as shown:
- In the Gene Ontology component, choose the type of GO term that one wants, either Component, Function or Process. In this example we will select the Function tab.
- Click on Map List(s).
- We see in the picture below that 49 of the 84 total genes were placed in functional categories. By scrolling and by clicking on individual tree nodes, we can explore the tree. We see that the largest single category, with 40 hits, was binding.
By clicking on the binding node, we can travel down to increasing levels of detail. By right-clicking on a folder or file icon and selecting Show Mappings->Selected List(including descendents) as shown below, we can see the gene names of the genes categorized at or below that level, here 25 involved in ATP binding.
A second view of the data is available by clicking on the TableView tab. This will show the degree of overrepresentation in GO categories. Here is the data for the Function category for the same list as above:
Here we see that the category with most significant overrepresentation is "microtubule motor activity".
Note the Save button at right on the component. This will dump the entire contents of the table to a text file with extension .dat.