Difference between revisions of "T-test"
(→Result Sets) |
(→Color Mosaic Controls) |
||
| Line 166: | Line 166: | ||
* '''Accession''' - When active, display the accession ids (probeset ids) for each marker at the right edge of the color mosaic. | * '''Accession''' - When active, display the accession ids (probeset ids) for each marker at the right edge of the color mosaic. | ||
* '''Label''' - When active, display the gene name for the marker is present in the annotation file. | * '''Label''' - When active, display the gene name for the marker is present in the annotation file. | ||
| − | * '''Sort''' - | + | * '''Sort''' - When depressed, applies an alternate sorting by fold-change and t-value. See description in [[Color_Mosaic|Color Mosaic]]. |
* '''Lightbulb''' [[Image:Color_Mosaic_Lightbulb.png]] - Activate the tooltip function over the color mosaic display. The tooltip displays the array name, the marker id, and the signal value from the array for the cell below the cursor. | * '''Lightbulb''' [[Image:Color_Mosaic_Lightbulb.png]] - Activate the tooltip function over the color mosaic display. The tooltip displays the array name, the marker id, and the signal value from the array for the cell below the cursor. | ||
* '''Search fields''' - These three search fields feature progressive search. As each character is typed in, the first match to the entered string will be automatically highlighted. The next match can be found by hitting the "Enter" key. Typing additional characters further narrows the search. Each search field is active only when the label it searches being displayed (corresponding button is activated). | * '''Search fields''' - These three search fields feature progressive search. As each character is typed in, the first match to the entered string will be automatically highlighted. The next match can be found by hitting the "Enter" key. Typing additional characters further narrows the search. Each search field is active only when the label it searches being displayed (corresponding button is activated). | ||
Revision as of 13:39, 7 June 2011
Overview
A t-Test analysis can be used to identify markers with statistically significant differential expression between two sets of microarrays. In geWorkbench, these groups are specified as the "Case" and "Control" sets.
There are several steps to setting up a t-test analysis in geWorkbench.
- At least two sets of arrays must be available in the Arrays component.
- The array sets to be used in the analysis must be "activated" by checking the box adjacent to their names in the Arrays component.
- One or more activated array sets must be designated "Case", and the others "Control" (which is the default classification).
- The t-test parameters must be set.
After the t-test is run, the results will be displayed graphically, and all markers meeting the significance threshold are placed into a new Marker Set called "Significant Genes".
Please see the Example section below for instructions on preparing array sets for the t-test analysis.
t-Test Parameters
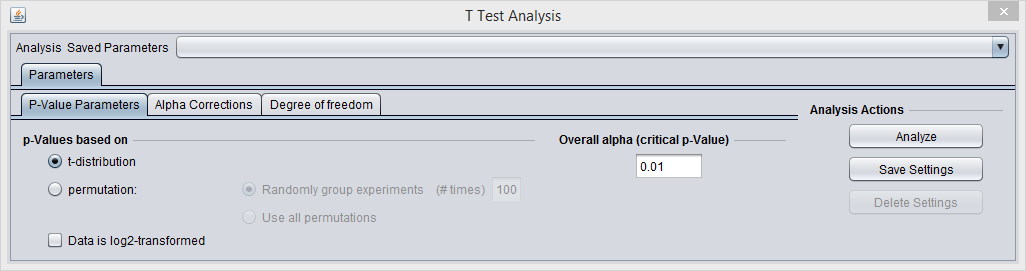
P-value Parameters
p-values based on
The p-values can be calculated by transforming the t-statistic directly, or by carrying out a permutation analysis. The permutation analysis measures how often a t-statistic at least as large as that observed occurs by chance after array labels of case and control are permuted.
- t-distribution (the default)
- Permutation - If chosen, the number of permutations to carry out must also be specified.
Overall alpha (Critical p-value)
The threshold for a difference in expression between Case and Control sets being called significant. A value of 0.05 is often used for a single test. Multiple-testing corrections can be specified in the Alpha Corrections tab.
Data is Log2-transformed
If the dataset has been Log2 transformed, check this box. Having this information allows the fold-change displayed in the Volcano Plot to be calculated in a consistent fashion.
The system will examine the current dataset and make a guess as to whether the data has been log2 transformed. The user can override this guess using the check box.
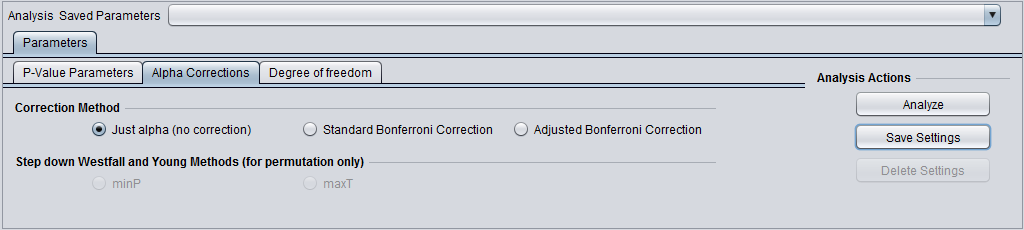
Alpha corrections
For multiple testing (alpha) correction, the following options are offered:
- no correction
- Standard Bonferonni Correction - the value of alpha is divided by the number of markers included in the analysis.
- Adjusted (step down) Bonferonni Correction
- Two variants of the Westfall and Young method are available if the p-value is estimated by permuation:
- minP
- maxT
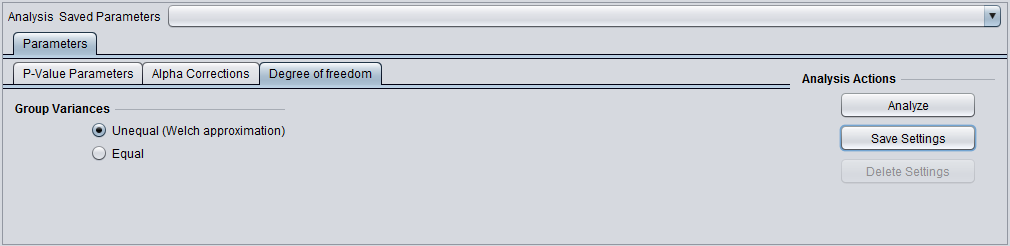
Degrees of Freedom
Group variances can be declared as:
- unequal (Welch approximation) (default)
- Equal.
Example
Preparation
Obtain the file "BCell-100.exp", which is contained in the data/public_data directory of the geWorkbench distribution, or can be directly downloaded from the tutorial data download area.
You may also wish to load the Affymetrix HG-U95Av2 annotation file, although it is not required for this example. See the FAQ section for information on downloading this file from Affymetrix.
For tips on loading data files, see Local Data Files and Projects.
In this example, we apply two normalization steps to the data set.
- Threshold Normalizer - set a minimum value of 1. Any value less than 1 will be set to 1.
- Log2 Transformation Normalizer - Log2 transform the data.
For an actual data analysis, you should apply data normalization steps appropriate to your own data and analysis design.
Array Classification
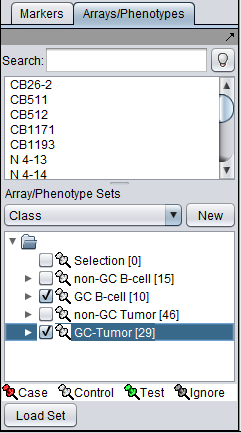
The t-test in geWorkbench requires that at least two sets of arrays be "activated". Only such "activated" sets are considered. In addition, at least one such set must be designated as "Case", and at least one other as "Control" (which is the default classification). Note that more than one set of arrays can be marked as "Case" or control.
Array set classification is covered in the Arrays/Phenotypes chapter. However, for convenience, the steps are illustrated here.
The desired sets of arrays should be activated in the Arrays/Phenotypes component. This is done by checking the boxes by the desired Sets.
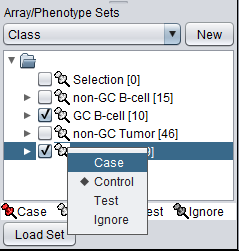
The classification can be made directly by left-clicking on the "thumb-tack" icon adjacent to an array set name.
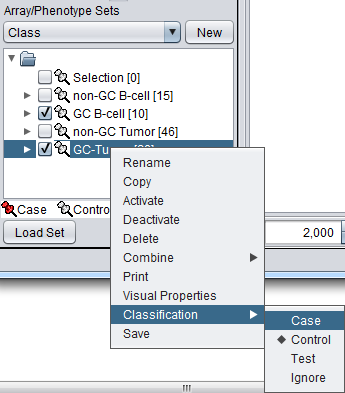
The array classification can also be set by right-clicking on the desired array set and selecting "Classification":
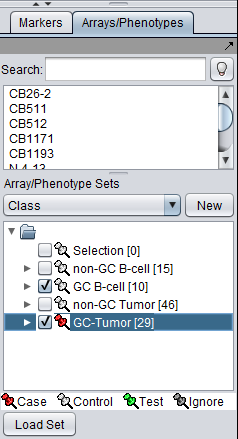
Using either method, the desired array set can be classified as "Case":
The thumbtack image next to activated Array Sets is colored red.
Seting the Analysis Parameters
- The t-test component should be loaded by default in the Component Configuration Manager.
- From the Analysis Panel, select T-Test Analysis.
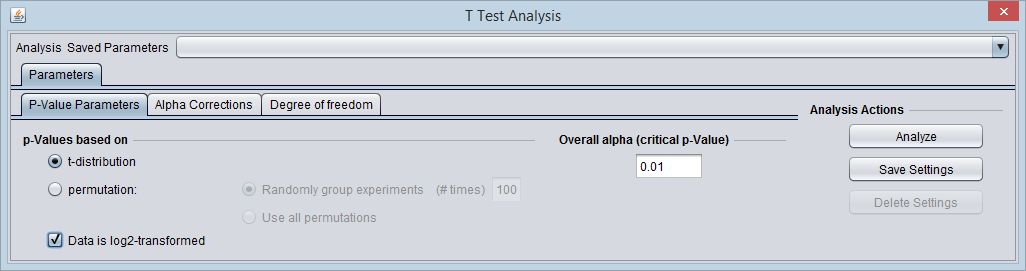
- P-value Parameters tab:
- P-values based on t-distribution.
- Note that here the default alpha (critical p-value) is set to 0.01.
- Check-mark the box "Data is log2 Transformed".
- Alpha-corrections tab
- Standard Bonferonni
- Degree of Freedom tab
- Welch approximation - unequal group variances.
The P-value Parameters tab set for the example analysis:
Running the t-test analysis
- Click Analyze. The results will be returned in three locations: The Project Folder, the Markers component, and the Visualization area.
t-Test Results
Result Sets
A t-test result node is placed into the Projects Folder as a child of the microarray dataset that was analyzed (upper red arrow).
The list of significant markers is placed into a new set in the Markers component (lower red arrow). This set is labeled "Significant Genes". The number in square brackets indicates the number of markers in the set.
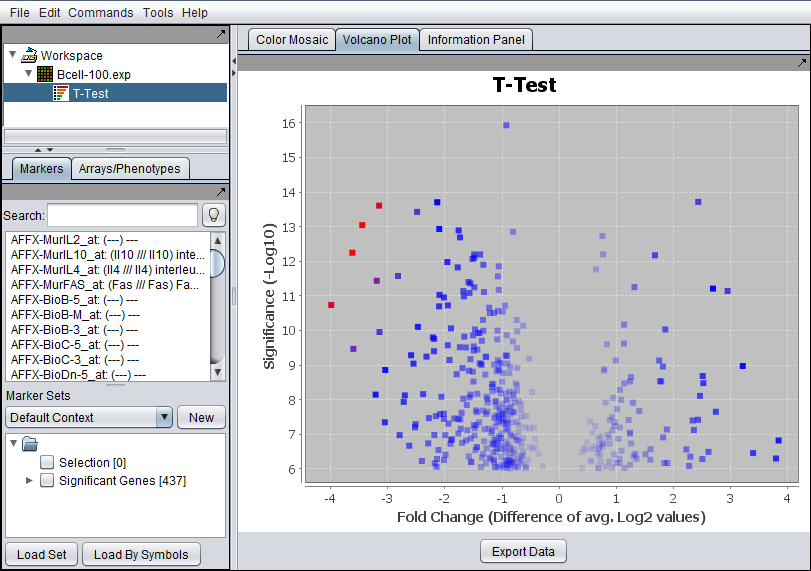
Volcano Plot Visualizer
The results are displayed in Volcano Plot visualizer (seen at right in the figure above).
Axes - The log2 fold change for each marker is plotted against the -log10 of the P-value.
Fold Change - The fold change is calculated, for each marker, as the average expression in the Case set divided by the average expression in the control set. If the data is known to already be log2 transformed, the antilog is first taken before averaging. The log2 of the ratio is then taken for use in the display.
Color scheme - the lower 2/3 of the absolute values of the (fold change) * (significance) are colored in shades from light blue (lowest values) to dark blue (highest values). The highest 1/3 of such values are colored from dark blue (lowest values) to red (highest values).
Export Data - The data depicted in the volcano plot is exported to a CSV format file. The column headers are: Probe Set Name, Gene Name, p-Value, Fold Change.
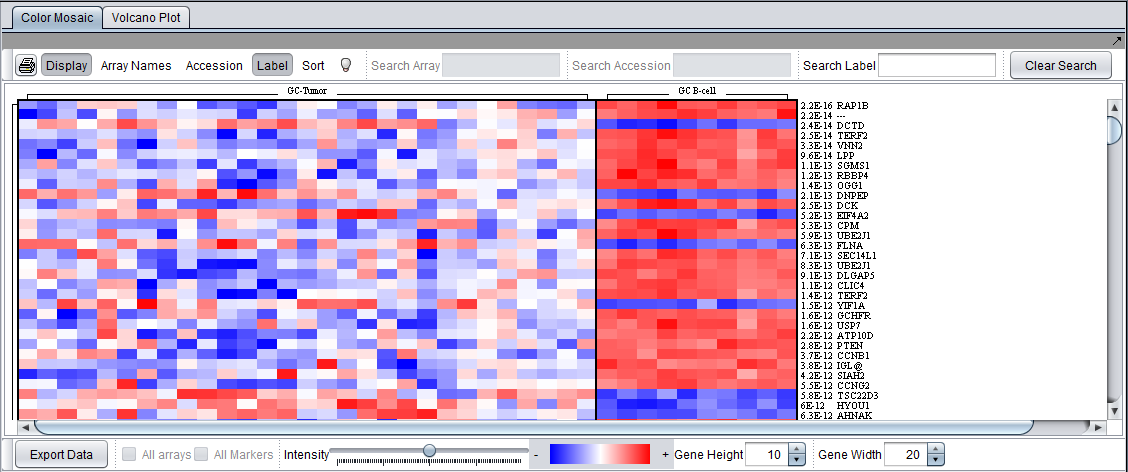
Color Mosaic Visualizer
The Color Mosaic tab shows all of the arrays and the p-value calculated for each marker. It also can display annotation for each marker.
Color Mosaic Controls
- Printer Icon - print
- Display - Turn the display on or off
- Array names - When active, display the array names along the top of the color mosaic display.
- Accession - When active, display the accession ids (probeset ids) for each marker at the right edge of the color mosaic.
- Label - When active, display the gene name for the marker is present in the annotation file.
- Sort - When depressed, applies an alternate sorting by fold-change and t-value. See description in Color Mosaic.
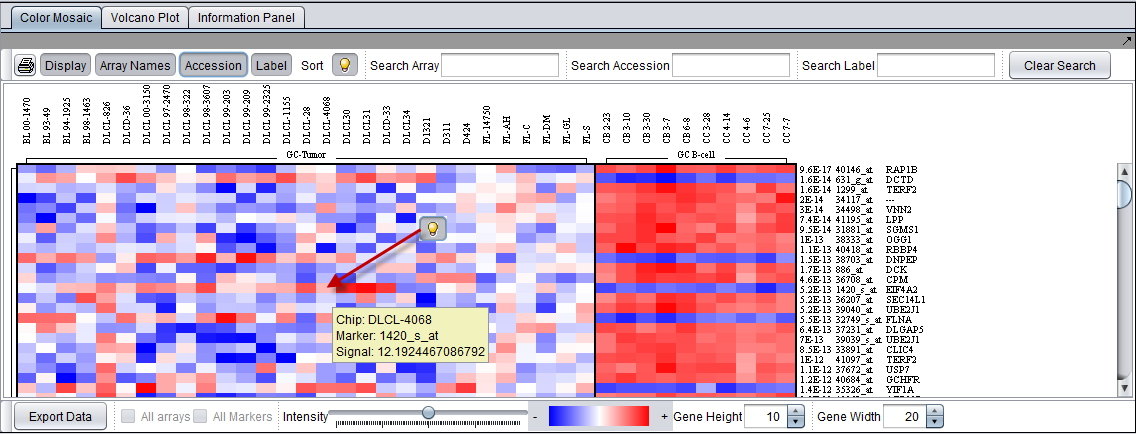
- Lightbulb
 - Activate the tooltip function over the color mosaic display. The tooltip displays the array name, the marker id, and the signal value from the array for the cell below the cursor.
- Activate the tooltip function over the color mosaic display. The tooltip displays the array name, the marker id, and the signal value from the array for the cell below the cursor. - Search fields - These three search fields feature progressive search. As each character is typed in, the first match to the entered string will be automatically highlighted. The next match can be found by hitting the "Enter" key. Typing additional characters further narrows the search. Each search field is active only when the label it searches being displayed (corresponding button is activated).
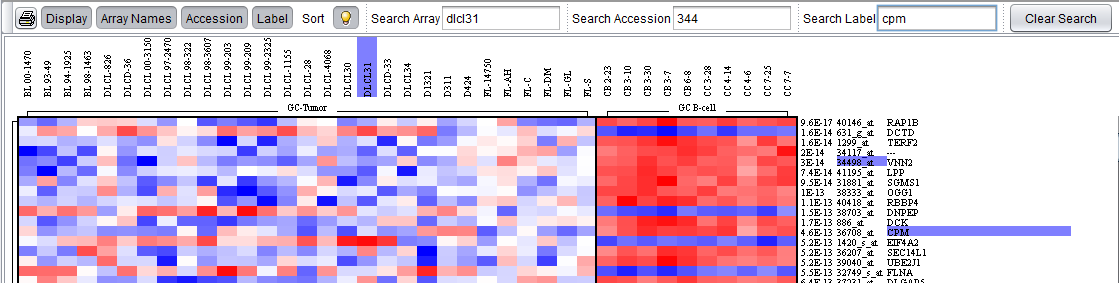
- Search Array - Searches Array Names when the Array names button is on.
- Search Accession - Searches Marker IDs when the Accession button is on.
- Search Label - Searches Gene Names when the Label button is on.
The figure below shows the effects of activating several of the display controls.
The controls for display of Array Name, Accession ID (probeset id) and the lightbulb tooltip control have been activated.
Search fields for each activated label type are enabled.
The tooltip displays the Array Name (chip), the marker id, and the signal value for the selected cell (array and marker) in the Color Mosaic display.
The figure below shows the results, with labels highlighted in purple, of searches using all three search fields.